Page 70 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 70
62 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
This chapter provides a brief overview of methods used to spin nearly
pure CNT fibers from carbon nanotubes suspended or dissolved in a solvent,
known as wet spinning or solution spinning. Carbon nanotubes cannot be
controlled and aligned in solution unless they are dispersed at the molecular
level, that is, single-nanotube level. A major challenge to the production of
neat CNT fibers is dispersing the CNTs at high enough concentration suit-
able for efficient alignment and effective coagulation [3]. Solution spinning
of CNT-based fibers is based on CNT dispersions stabilized in surfactant
solution, superacids or other solvents.
4.2 Spinning from surfactant-based solutions
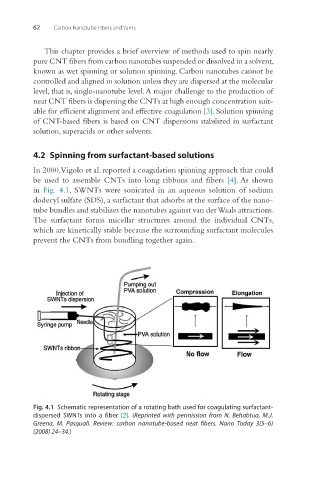
In 2000, Vigolo et al. reported a coagulation spinning approach that could
be used to assemble CNTs into long ribbons and fibers [4]. As shown
in Fig. 4.1, SWNTs were sonicated in an aqueous solution of sodium
dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a surfactant that adsorbs at the surface of the nano-
tube bundles and stabilizes the nanotubes against van der Waals attractions.
The surfactant forms micellar structures around the individual CNTs,
which are kinetically stable because the surrounding surfactant molecules
prevent the CNTs from bundling together again.
Fig. 4.1 Schematic representation of a rotating bath used for coagulating surfactant-
dispersed SWNTs into a fiber [2]. (Reprinted with permission from N. Behabtua, M.J.
Greena, M. Pasquali. Review: carbon nanotube-based neat fibers. Nano Today 3(5–6)
(2008) 24–34.)