Page 55 - Carbonate Sedimentology and Sequence Stratigraphy
P. 55
46 WOLFGANG SCHLAGER
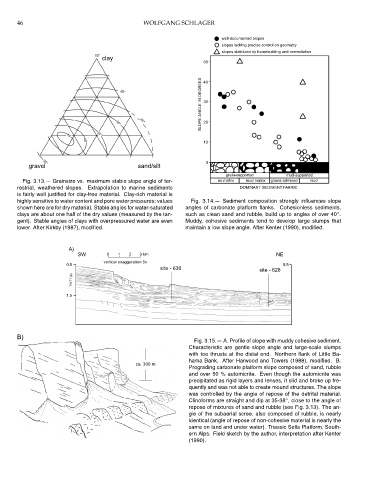
well-documented slopes
slopes lacking precise control on geometry
slopes stabilized by framebuilding and cementation
10°
clay
50
SLOPE ANGLE IN DEGREES 30
20° 40
20
25°
30°
35°
45
10
40°
0
35°
gravel sand/silt
grain-supported mud-supported
Fig. 3.13.— Grainsize vs. maximum stable slope angle of ter- no matrix mud matrix grains admixed mud
restrial, weathered slopes. Extrapolation to marine sediments DOMINANT SEDIMENT FABRIC
is fairly well justified for clay-free material. Clay-rich material is
highly sensitive to water content and pore water pressures; values Fig. 3.14.— Sediment composition strongly influences slope
shown here are for dry material. Stable angles for water-saturated angles of carbonate platform flanks. Cohesionless sediments,
◦
clays are about one half of the dry values (measured by the tan- such as clean sand and rubble, build up to angles of over 40 .
gent). Stable angles of clays with overpressured water are even Muddy, cohesive sediments tend to develop large slumps that
lower. After Kirkby (1987), modified. maintain a low slope angle. After Kenter (1990), modified.
A)
SW 0 1 2 3 km NE
vertical exaggeration 5x
0.5 0.5
site - 630 site - 628
TWTT (s)
1.5
B)
Fig. 3.15.— A. Profile of slope with muddy cohesive sediment.
Characteristic are gentle slope angle and large-scale slumps
with toe thrusts at the distal end. Northern flank of Little Ba-
hama Bank. After Harwood and Towers (1988), modified. B.
ca. 300 m
Prograding carbonate platform slope composed of sand, rubble
and over 50 % automicrite. Even though the automicrite was
precipitated as rigid layers and lenses, it slid and broke up fre-
quently and was not able to create mound structures. The slope
was controlled by the angle of repose of the detrital material.
◦
Clinoforms are straight and dip at 35-38 , close to the angle of
repose of mixtures of sand and rubble (see Fig. 3.13). The an-
gle of the subaerial scree, also composed of rubble, is nearly
identical (angle of repose of non-cohesive material is nearly the
same on land and under water). Triassic Sella Platform, South-
ern Alps. Field sketch by the author, interpretation after Kenter
(1990).