Page 421 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 421
384 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
The ML L’ species is often called an outer sphere complex, or, if ML is a cation and L an anion,
3 4
the couple is called an ion pair.
For the I mechanism, associative interchange, the interaction between M and L’ is more advanced
a
. . . .
in the transition state than in the case of the I . The M L’ bonding is important in defi ning the
d
activated complex. Both of these interchange mechanisms are loosely connected to the S 2-type
N
mechanism.
For the A mechanism, associative, there is a fully formed intermediate complex ML L’, which
4
then dissociates, being roughly analogous to the E type reaction mechanism.
1
It is important to remember that the same electronic, steric, mechanistic, kinetic, and thermody-
namic factors that operate in regard to smaller molecules are in operation during a polymerization
process.
11.3 CONDENSATION ORGANOMETALLIC POLYMERS
Condensation reactions exhibit several characteristics such as (typically) expulsion of a smaller mol-
ecule on reaction leading to a repeat unit containing fewer atoms than the sum of the two reactants,
and most reactions can be considered in terms of polar (Lewis acid–base; nucleophilic–electro-
philic) mechanisms. The reaction site can be at the metal atom (i.e., adjacent to the atom)
R MX + H N–R–NH → –(–MR –NH–R–NH–)– + HX (11.6)
2 2 2 2 2
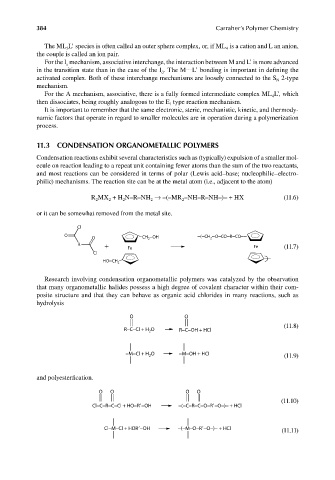
or it can be somewhat removed from the metal site.
Cl
O −(−CH −O−CO−R−CO−−
O CH −OH 2
2
R + Fe Fe (11.7)
Cl
HO−CH
2
Research involving condensation organometallic polymers was catalyzed by the observation
that many organometallic halides possess a high degree of covalent character within their com-
posite structure and that they can behave as organic acid chlorides in many reactions, such as
hydrolysis
O O
(11.8)
R−C−Cl + H O R−C−OH + HCl
2
−M−Cl + H O −M−OH + HCI (11.9)
2
and polyesterfi cation.
O O O O
(11.10)
Cl−C−R−C−Cl + HO−R −OH −(−C−R−C−O−R −O−)− + HCl
Cl−M−Cl + HOR −OH −(−M−O−R −O−)− + HCl
(11.11)
9/14/2010 3:41:35 PM
K10478.indb 384
K10478.indb 384 9/14/2010 3:41:35 PM