Page 600 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 600
Synthesis of Reactants and Intermediates for Polymers 563
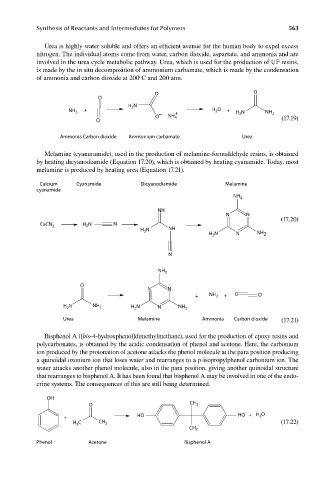
Urea is highly water soluble and offers an efficient avenue for the human body to expel excess
nitrogen. The individual atoms come from water, carbon dioxide, aspartate, and ammonia and are
involved in the urea cycle metabolic pathway. Urea, which is used for the production of UF resins,
is made by the in situ decomposition of ammonium carbamate, which is made by the condensation
o
of ammonia and carbon dioxide at 200 C and 200 atm.
O O
O
N
H 2
NH 3 + − + H 2 O + H 2 N NH 2
O NH 4
O (17.19)
Ammonia Carbon dioxide Ammonium carbamate Urea
Melamine (cyanuramide), used in the production of melamine-formaldehyde resins, is obtained
by heating dicyanodiamide (Equation 17.20), which is obtained by heating cyanamide. Today, most
melamine is produced by heating urea (Equation 17.21).
Calcium Cyanamide Dicyanodiamide Melamine
cyanamide
NH 2
NH
N N
(17.20)
CaCN 2 H N N
2
H N NH H N N NH 2
3
2
N
NH 2
O
N N
+ NH 2 + O O
H N NH 2 H 2 N N NH 2
2
Urea Melamine Ammonia Carbon dioxide (17.21)
Bisphenol A ([bis-4-hydroxphenol]dimethylmethane), used for the production of epoxy resins and
polycarbonates, is obtained by the acidic condensation of phenol and acetone. Here, the carbonium
ion produced by the protonation of acetone attacks the phenol molecule at the para position producing
a quinoidal oxonium ion that loses water and rearranges to a p-isopropylphenol carbonium ion. The
water attacks another phenol molecule, also in the para position, giving another quinoidal structure
that rearranges to bisphenol A. It has been found that bisphenol A may be involved in one of the endo-
crine systems. The consequences of this are still being determined.
OH
O CH 3
2
+ HO HO + H O
H C CH 3 (17.22)
3
CH 3
Phenol Acetone Bisphenol A
9/14/2010 3:43:23 PM
K10478.indb 563 9/14/2010 3:43:23 PM
K10478.indb 563