Page 141 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 141
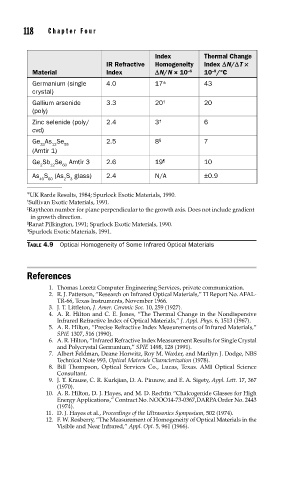
118 Cha pte r F o u r
Index Thermal Change
IR Refractive Homogeneity Index DN/DT ¥
Material Index DN/N × 10 –6 10 /°C
–5
Germanium (single 4.0 17∗ 43
crystal)
Gallium arsenide 3.3 20 † 20
(poly)
Zinc selenide (poly/ 2.4 3 ‡ 6
cvd)
Ge As Se 2.5 8 § 7
33 12 55
(Amtir 1)
Ge Sb Se Amtir 3 2.6 19 ¶ 10
2 12 60
As S (As S glass) 2.4 N/A ±0.9
40 60 2 3
∗ UK Rarde Results, 1984; Spurlock Exotic Materials, 1990.
† Sullivan Exotic Materials, 1991.
‡ Raytheon number for plane perpendicular to the growth axis. Does not include gradient
in growth direction.
§ Ranat Pilkington, 1991; Spurlock Exotic Materials, 1990.
¶ Spurlock Exotic Materials, 1991.
TABLE 4.9 Optical Homogeneity of Some Infrared Optical Materials
References
1. Thomas Loretz Computer Engineering Services, private communication.
2. R. J. Patterson, “Research on Infrared Optical Materials,” TI Report No. AFAL-
TR-66, Texas Instruments, November 1966.
3. J. T. Littleton, J. Amer. Ceramic Soc. 10, 259 (1927).
4. A. R. Hilton and C. E. Jones, “The Thermal Change in the Nondispersive
Infrared Refractive Index of Optical Materials,” J. Appl. Phys. 6, 1513 (1967).
5. A. R. Hilton, “Precise Refractive Index Measurements of Infrared Materials,”
SPIE 1307, 516 (1990).
6. A. R. Hilton, “Infrared Refractive Index Measurement Results for Single Crystal
and Polycrystal Germanium,” SPIE 1498, 128 (1991).
7. Albert Feldman, Deane Horwitz, Roy M. Waxler, and Marilyn J. Dodge, NBS
Technical Note 993, Optical Materials Characterization (1978).
8. Bill Thompson, Optical Services Co., Lucas, Texas. AMI Optical Science
Consultant.
9. J. T. Krause, C. R. Kurkjian, D. A. Pinnow, and E. A. Sigety, Appl. Lett. 17, 367
(1970).
10. A. R. Hilton, D. J. Hayes, and M. D. Rechtin “Chalcogenide Glasses for High
Energy Applications,” Contract No. NOOO14-73-0367,DARPA Order No. 2443
(1974).
11. D. J. Hayes et al., Proceedings of the Ultrasonics Symposium, 502 (1974).
12. F. W. Rosberry, “The Measurement of Homogeneity of Optical Materials in the
Visible and Near Infrared,” Appl. Opt. 5, 961 (1966).