Page 181 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 181
Glass Pr ocesses for Other Applications 157
0.4 690
Absorption temperature 680
Absorption coefficient (cm –1 ) 0.2 670 Top temperature (°C)
coefficient
Head
0.3
0.1
650
0 660
0 20 40 60 80 100
% Fraction of liquid distillate
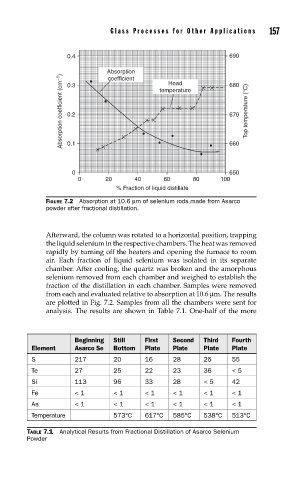
FIGURE 7.2 Absorption at 10.6 µm of selenium rods made from Asarco
powder after fractional distillation.
Afterward, the column was rotated to a horizontal position, trapping
the liquid selenium in the respective chambers. The heat was removed
rapidly by turning off the heaters and opening the furnace to room
air. Each fraction of liquid selenium was isolated in its separate
chamber. After cooling, the quartz was broken and the amorphous
selenium removed from each chamber and weighed to establish the
fraction of the distillation in each chamber. Samples were removed
from each and evaluated relative to absorption at 10.6 µm. The results
are plotted in Fig. 7.2. Samples from all the chambers were sent for
analysis. The results are shown in Table 7.1. One-half of the more
Beginning Still First Second Third Fourth
Element Asarco Se Bottom Plate Plate Plate Plate
S 217 20 16 28 25 55
Te 27 25 22 23 36 < 5
Si 113 96 33 28 < 5 42
Fe < 1 < 1 < 1 < 1 < 1 < 1
As < 1 < 1 < 1 < 1 < 1 < 1
Temperature 573°C 617°C 585°C 538°C 513°C
TABLE 7.1 Analytical Results from Fractional Distillation of Asarco Selenium
Powder