Page 197 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 197
Glass Pr ocesses for Other Applications 173
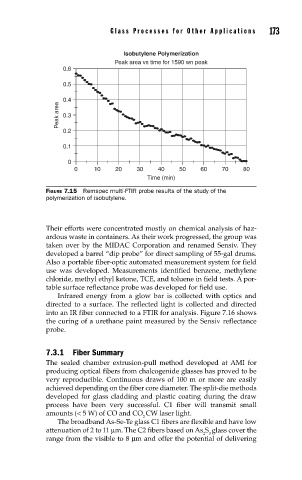
Isobutylene Polymerization
Peak area vs time for 1590 wn peak
0.6
0.5
Peak area 0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Time (min)
FIGURE 7.15 Remspec multi-FTIR probe results of the study of the
polymerization of isobutylene.
Their efforts were concentrated mostly on chemical analysis of haz-
ardous waste in containers. As their work progressed, the group was
taken over by the MIDAC Corporation and renamed Sensiv. They
developed a barrel “dip probe” for direct sampling of 55-gal drums.
Also a portable fiber-optic automated measurement system for field
use was developed. Measurements identified benzene, methylene
chloride, methyl ethyl ketone, TCE, and toluene in field tests. A por-
table surface reflectance probe was developed for field use.
Infrared energy from a glow bar is collected with optics and
directed to a surface. The reflected light is collected and directed
into an IR fiber connected to a FTIR for analysis. Figure 7.16 shows
the curing of a urethane paint measured by the Sensiv reflectance
probe.
7.3.1 Fiber Summary
The sealed chamber extrusion-pull method developed at AMI for
producing optical fibers from chalcogenide glasses has proved to be
very reproducible. Continuous draws of 100 m or more are easily
achieved depending on the fiber core diameter. The split-die methods
developed for glass cladding and plastic coating during the draw
process have been very successful. C1 fiber will transmit small
amounts (< 5 W) of CO and CO CW laser light.
2
The broadband As-Se-Te glass C1 fibers are flexible and have low
attenuation of 2 to 11 µm. The C2 fibers based on As S glass cover the
2 3
range from the visible to 8 µm and offer the potential of delivering