Page 147 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 147
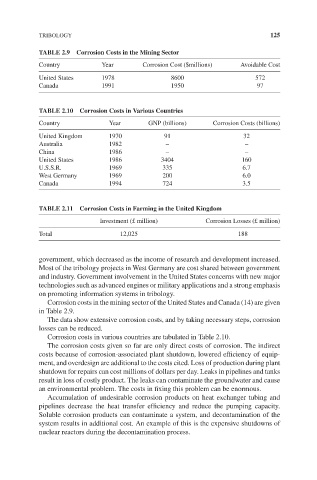
TRIBOLOGY 125
TABLE 2.9 Corrosion Costs in the Mining Sector
Country Year Corrosion Cost ($millions) Avoidable Cost
United States 1978 8600 572
Canada 1991 1950 97
TABLE 2.10 Corrosion Costs in Various Countries
Country Year GNP (billions) Corrosion Costs (billions)
United Kingdom 1970 91 32
Australia 1982 – –
China 1986 – –
United States 1986 3404 160
U.S.S.R. 1969 335 6.7
West Germany 1969 200 6.0
Canada 1994 724 3.5
TABLE 2.11 Corrosion Costs in Farming in the United Kingdom
Investment (£ million) Corrosion Losses (£ million)
Total 12,025 188
government, which decreased as the income of research and development increased.
Most of the tribology projects in West Germany are cost shared between government
and industry. Government involvement in the United States concerns with new major
technologies such as advanced engines or military applications and a strong emphasis
on promoting information systems in tribology.
Corrosion costs in the mining sector of the United States and Canada (14) are given
in Table 2.9.
The data show extensive corrosion costs, and by taking necessary steps, corrosion
losses can be reduced.
Corrosion costs in various countries are tabulated in Table 2.10.
The corrosion costs given so far are only direct costs of corrosion. The indirect
costs because of corrosion-associated plant shutdown, lowered efficiency of equip-
ment, and overdesign are additional to the costs cited. Loss of production during plant
shutdown for repairs can cost millions of dollars per day. Leaks in pipelines and tanks
result in loss of costly product. The leaks can contaminate the groundwater and cause
an environmental problem. The costs in fixing this problem can be enormous.
Accumulation of undesirable corrosion products on heat exchanger tubing and
pipelines decrease the heat transfer efficiency and reduce the pumping capacity.
Soluble corrosion products can contaminate a system, and decontamination of the
system results in additional cost. An example of this is the expensive shutdowns of
nuclear reactors during the decontamination process.