Page 175 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 175
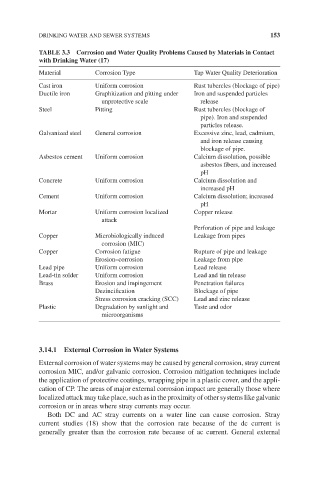
DRINKING WATER AND SEWER SYSTEMS 153
TABLE 3.3 Corrosion and Water Quality Problems Caused by Materials in Contact
with Drinking Water (17)
Material Corrosion Type Tap Water Quality Deterioration
Cast iron Uniform corrosion Rust tubercles (blockage of pipe)
Ductile iron Graphitization and pitting under Iron and suspended particles
unprotective scale release
Steel Pitting Rust tubercles (blockage of
pipe). Iron and suspended
particles release.
Galvanized steel General corrosion Excessive zinc, lead, cadmium,
and iron release causing
blockage of pipe.
Asbestos cement Uniform corrosion Calcium dissolution, possible
asbestos fibers, and increased
pH
Concrete Uniform corrosion Calcium dissolution and
increased pH
Cement Uniform corrosion Calcium dissolution; increased
pH
Mortar Uniform corrosion localized Copper release
attack
Perforation of pipe and leakage
Copper Microbiologically induced Leakage from pipes
corrosion (MIC)
Copper Corrosion fatigue Rupture of pipe and leakage
Erosion–corrosion Leakage from pipe
Lead pipe Uniform corrosion Lead release
Lead-tin solder Uniform corrosion Lead and tin release
Brass Erosion and impingement Penetration failures
Dezincification Blockage of pipe
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) Lead and zinc release
Plastic Degradation by sunlight and Taste and odor
microorganisms
3.14.1 External Corrosion in Water Systems
External corrosion of water systems may be caused by general corrosion, stray current
corrosion MIC, and/or galvanic corrosion. Corrosion mitigation techniques include
the application of protective coatings, wrapping pipe in a plastic cover, and the appli-
cation of CP. The areas of major external corrosion impact are generally those where
localized attack may take place, such as in the proximity of other systems like galvanic
corrosion or in areas where stray currents may occur.
Both DC and AC stray currents on a water line can cause corrosion. Stray
current studies (18) show that the corrosion rate because of the dc current is
generally greater than the corrosion rate because of ac current. General external