Page 244 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 244
222 CORROSION CONTROL AND PREVENTION
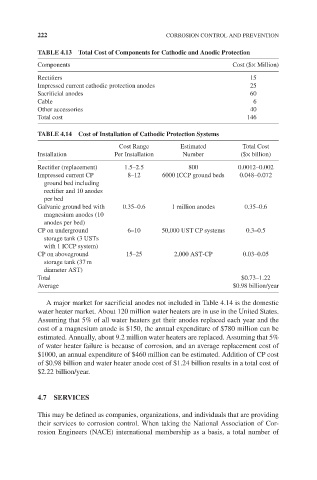
TABLE 4.13 Total Cost of Components for Cathodic and Anodic Protection
Components Cost ($× Million)
Rectifiers 15
Impressed current cathodic protection anodes 25
Sacrificial anodes 60
Cable 6
Other accessories 40
Total cost 146
TABLE 4.14 Cost of Installation of Cathodic Protection Systems
Cost Range Estimated Total Cost
Installation Per Installation Number ($× billion)
Rectifier (replacement) 1.5–2.5 800 0.0012–0.002
Impressed current CP 8–12 6000 ICCP ground beds 0.048–0.072
ground bed including
rectifier and 10 anodes
per bed
Galvanic ground bed with 0.35–0.6 1 million anodes 0.35–0.6
magnesium anodes (10
anodes per bed)
CP on underground 6–10 50,000 UST CP systems 0.3–0.5
storage tank (3 USTs
with 1 ICCP system)
CP on aboveground 15–25 2,000 AST-CP 0.03–0.05
storage tank (37 m
diameter AST)
Total $0.73–1.22
Average $0.98 billion/year
A major market for sacrificial anodes not included in Table 4.14 is the domestic
water heater market. About 120 million water heaters are in use in the United States.
Assuming that 5% of all water heaters get their anodes replaced each year and the
cost of a magnesium anode is $150, the annual expenditure of $780 million can be
estimated. Annually, about 9.2 million water heaters are replaced. Assuming that 5%
of water heater failure is because of corrosion, and an average replacement cost of
$1000, an annual expenditure of $460 million can be estimated. Addition of CP cost
of $0.98 billion and water heater anode cost of $1.24 billion results in a total cost of
$2.22 billion/year.
4.7 SERVICES
This may be defined as companies, organizations, and individuals that are providing
their services to corrosion control. When taking the National Association of Cor-
rosion Engineers (NACE) international membership as a basis, a total number of