Page 283 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 283
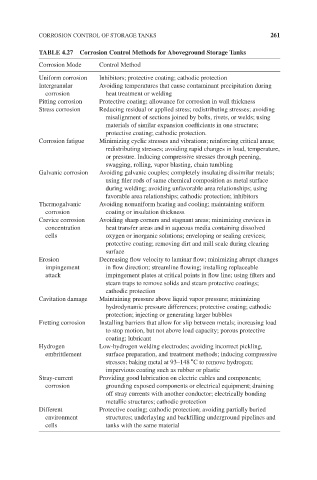
CORROSION CONTROL OF STORAGE TANKS 261
TABLE 4.27 Corrosion Control Methods for Aboveground Storage Tanks
Corrosion Mode Control Method
Uniform corrosion Inhibitors; protective coating; cathodic protection
Intergranular Avoiding temperatures that cause contaminant precipitation during
corrosion heat treatment or welding
Pitting corrosion Protective coating; allowance for corrosion in wall thickness
Stress corrosion Reducing residual or applied stress; redistributing stresses; avoiding
misalignment of sections joined by bolts, rivets, or welds; using
materials of similar expansion coefficients in one structure;
protective coating; cathodic protection.
Corrosion fatigue Minimizing cyclic stresses and vibrations; reinforcing critical areas;
redistributing stresses; avoiding rapid changes in load, temperature,
or pressure. Inducing compressive stresses through peening,
swagging, rolling, vapor blasting, chain tumbling
Galvanic corrosion Avoiding galvanic couples; completely insulating dissimilar metals;
using filer rods of same chemical composition as metal surface
during welding; avoiding unfavorable area relationships; using
favorable area relationships; cathodic protection; inhibitors
Thermogalvanic Avoiding nonuniform heating and cooling; maintaining uniform
corrosion coating or insulation thickness
Crevice corrosion Avoiding sharp corners and stagnant areas; minimizing crevices in
concentration heat transfer areas and in aqueous media containing dissolved
cells oxygen or inorganic solutions; enveloping or sealing crevices;
protective coating; removing dirt and mill scale during clearing
surface
Erosion Decreasing flow velocity to laminar flow; minimizing abrupt changes
impingement in flow direction; streamline flowing; installing replaceable
attack impingement plates at critical points in flow line; using filters and
steam traps to remove solids and steam protective coatings;
cathodic protection
Cavitation damage Maintaining pressure above liquid vapor pressure; minimizing
hydrodynamic pressure differences; protective coating; cathodic
protection; injecting or generating larger bubbles
Fretting corrosion Installing barriers that allow for slip between metals; increasing load
to stop motion, but not above load capacity; porous protective
coating; lubricant
Hydrogen Low-hydrogen welding electrodes; avoiding incorrect pickling,
embrittlement surface preparation, and treatment methods; inducing compressive
∘
stresses; baking metal at 93–148 C to remove hydrogen;
impervious coating such as rubber or plastic
Stray-current Providing good lubrication on electric cables and components;
corrosion grounding exposed components or electrical equipment; draining
off stray currents with another conductor; electrically bonding
metallic structures; cathodic protection
Different Protective coating; cathodic protection; avoiding partially buried
environment structures; underlaying and backfilling underground pipelines and
cells tanks with the same material