Page 367 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 367
CORROSION DAMAGE, DEFECTS, AND FAILURES 345
DOM.
CW LINE
HW sto. tank–1 HW sto. tank–2
C.V. C.V.
HW recirc.
pump
LP steam LP steam
Heat HW recirc. Heat
exchanger–1 line exchanger–2
Cond. F&T TRAP
Condensate
tank
Condensate
pumps
Pumped
condensate
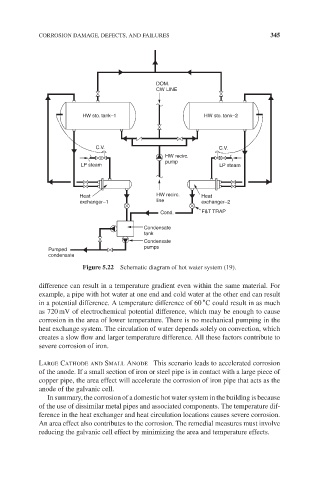
Figure 5.22 Schematic diagram of hot water system (19).
difference can result in a temperature gradient even within the same material. For
example, a pipe with hot water at one end and cold water at the other end can result
∘
in a potential difference. A temperature difference of 60 C could result in as much
as 720 mV of electrochemical potential difference, which may be enough to cause
corrosion in the area of lower temperature. There is no mechanical pumping in the
heat exchange system. The circulation of water depends solely on convection, which
creates a slow flow and larger temperature difference. All these factors contribute to
severe corrosion of iron.
Large Cathode and Small Anode This scenario leads to accelerated corrosion
of the anode. If a small section of iron or steel pipe is in contact with a large piece of
copper pipe, the area effect will accelerate the corrosion of iron pipe that acts as the
anode of the galvanic cell.
In summary, the corrosion of a domestic hot water system in the building is because
of the use of dissimilar metal pipes and associated components. The temperature dif-
ference in the heat exchanger and heat circulation locations causes severe corrosion.
An area effect also contributes to the corrosion. The remedial measures must involve
reducing the galvanic cell effect by minimizing the area and temperature effects.