Page 71 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions
P. 71
T1: IML
P2: —/—
QC: —/—
P1: KVU/—
AT029-02
16:6
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
AT029-Manual
August 16, 2007
2. CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PURE HYDROCARBONS 51
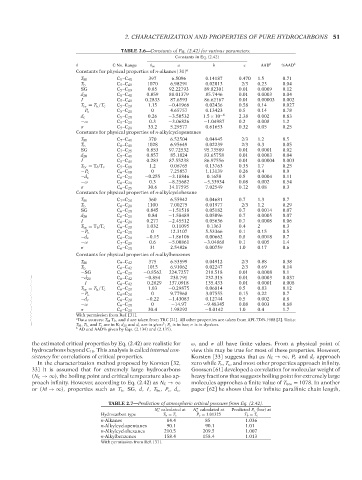
TABLE 2.6—Constants of Eq. (2.42) for various parameters.
Constants in Eq. (2.42)
θ C No. Range θ ∞ a b c AAD b %AAD b
Constants for physical properties of n-alkanes [31] a
T M C 5 –C 40 397 6.5096 0.14187 0.470 1.5 0.71
T b C 5 –C 40 1070 6.98291 0.02013 2/3 0.23 0.04
SG C 5 –C 19 0.85 92.22793 89.82301 0.01 0.0009 0.12
d 20 C 5 –C 40 0.859 88.01379 85.7446 0.01 0.0003 0.04
I C 5 –C 40 0.2833 87.6593 86.62167 0.01 0.00003 0.002
T br = T b /T c C 5 –C 20 1.15 −0.41966 0.02436 0.58 0.14 0.027
−P c C 5 –C 20 0 4.65757 0.13423 0.5 0.14 0.78
d c C 5 –C 20 0.26 −3.50532 1.5 × 10 −6 2.38 0.002 0.83
−ω C 5 –C 20 0.3 −3.06826 −1.04987 0.2 0.008 1.2
σ C 5 –C 20 33.2 5.29577 0.61653 0.32 0.05 0.25
Constants for physical properties of n-alkylcyclopentanes
T M C 7 –C 41 370 6.52504 0.04945 2/3 1.2 0.5
T b C 6 –C 41 1028 6.95649 0.02239 2/3 0.3 0.05
SG C 7 –C 25 0.853 97.72532 95.73589 0.01 0.0001 0.02
d 20 C 5 –C 41 0.857 85.1824 83.65758 0.01 0.0003 0.04
I C 5 –C 41 0.283 87.55238 86.97556 0.01 0.00004 0.003
T br = T b /T c C 5 –C 18 1.2 0.06765 0.13763 0.35 1.7 0.25
−P c C 6 –C 18 0 7.25857 1.13139 0.26 0.4 0.9
−d c C 6 –C 20 −0.255 −3.18846 0.1658 0.5 0.0004 0.11
−ω C 6 –C 20 0.3 −8.25682 −5.33934 0.08 0.002 0.54
σ C 6 –C 25 30.6 14.17595 7.02549 0.12 0.08 0.3
Constants for physical properties of n-alkylcyclohexane
T M C 7 –C 20 360 6.55942 0.04681 0.7 1.3 0.7
T b C 6 –C 20 1100 7.00275 0.01977 2/3 1.2 0.29
SG C 6 –C 20 0.845 −1.51518 0.05182 0.7 0.0014 0.07
d 20 C 6 –C 21 0.84 −1.58489 0.05096 0.7 0.0005 0.07
I C 6 –C 20 0.277 −2.45512 0.05636 0.7 0.0008 0.06
T br = T b /T c C 6 –C 20 1.032 −0.11095 0.1363 0.4 2 0.3
−P c C 6 –C 20 0 12.3107 5.53366 0.1 0.15 0.5
−d c C 6 –C 20 −0.15 −1.86106 0.00662 0.8 0.0018 0.7
−ω C 7 –C 20 0.6 −5.00861 −3.04868 0.1 0.005 1.4
σ C 6 –C 20 31 2.54826 0.00759 1.0 0.17 0.6
Constants for physical properties of n-alkylbenzenes
T M C 9 –C 42 375 6.53599 0.04912 2/3 0.88 0.38
T b C 6 –C 42 1015 6.91062 0.02247 2/3 0.69 0.14
−SG C 6 –C 20 −0.8562 224.7257 218.518 0.01 0.0008 0.1
−d 20 C 6 –C 42 −0.854 238.791 232.315 0.01 0.0003 0.037
−I C 6 –C 42 −0.2829 137.0918 135.433 0.01 0.0001 0.008
T br = T b /T c C 6 –C 20 1.03 −0.29875 0.06814 0.5 0.83 0.12
−P c C 6 –C 20 0 9.77968 3.07555 0.15 0.22 0.7
−d c C 6 –C 20 −0.22 −1.43083 0.12744 0.5 0.002 0.8
−ω C 6 –C 20 0 −14.97 −9.48345 0.08 0.003 0.68
σ C 6 –C 20 30.4 1.98292 −0.0142 1.0 0.4 1.7
With permission from Ref. [31].
a Data sources: T M T b , and d are taken from TRC [21]. All other properties are taken from API-TDB-1988 [2]. Units:
3
T M , T b, and T c are in K; d 20 and d c are in g/cm ; P c is in bar; σ is in dyn/cm.
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
b AD and AAD% given by Eqs. (2.134) and (2.135).
the estimated critical properties by Eq. (2.42) are realistic for ω, and σ all have finite values. From a physical point of
hydrocarbons beyond C 18 . This analysis is called internal con- view this may be true for most of these properties. However,
sistency for correlations of critical properties. Korsten [33] suggests that as N C →∞, P c and d c approach
In the characterization method proposed by Korsten [32, zero while T b , T c , and most other properties approach infinity.
33] it is assumed that for extremely large hydrocarbons Goossen [61] developed a correlation for molecular weight of
(N C →∞), the boiling point and critical temperature also ap- heavy fractions that suggests boiling point for extremely large
proach infinity. However, according to Eq. (2.42) as N C →∞ molecules approches a finite value of T b∞ = 1078. In another
or (M →∞), properties such as T b , SG, d, I, T br , P c , d c , paper [62] he shows that for infinite paraffinic chain length,
TABLE 2.7—Prediction of atmospheric critical pressure from Eq. (2.42).
N c calculated at N c calculated at Predicted P c (bar) at
∗
∗
Hydrocarbon type T b = T c P c = 1.01325 T b = T c
n-Alkanes 84.4 85 1.036
n-Alkylcyclopentanes 90.1 90.1 1.01
n-Alkylcyclohexanes 210.5 209.5 1.007
n-Alkylbenzenes 158.4 158.4 1.013
With permission from Ref. [31].
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT