Page 76 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions
P. 76
P2: —/—
T1: IML
P1: KVU/—
QC: —/—
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
AT029-Manual
AT029-02
56 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
n August 16, 2007 16:6
alkane
Molecular Weight
Specific Gravity
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
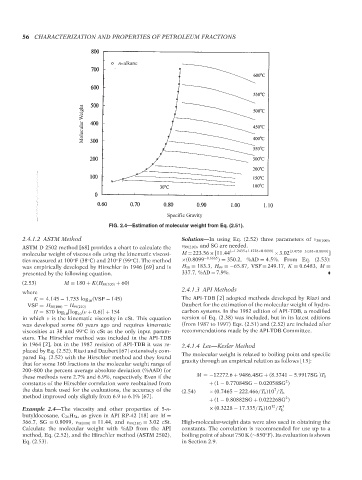
FIG. 2.4—Estimation of molecular weight from Eq. (2.51).
2.4.1.2 ASTM Method Solution—In using Eq. (2.52) three parameters of ν 38(100) ,
ASTM D 2502 method [68] provides a chart to calculate the ν 99(210) , and SG are needed.
(−1.2435+1.1228×0.8099)
molecular weight of viscous oils using the kinematic viscosi- M = 223.56×[11.44 ×3.02 (3.4758−3.038×0.8099) ]
ties measured at 100 F (38 C) and 210 F (99 C). The method ×(0.8099 −0.6665 ) = 350.2, %AD = 4.5%. From Eq. (2.53):
◦
◦
◦
◦
was empirically developed by Hirschler in 1946 [69] and is H 38 = 183.3, H 99 =−65.87, VSF = 249.17, K = 0.6483, M =
presented by the following equation. 337.7, %AD = 7.9%.
(2.53) M = 180 + K(H 38(100) + 60)
2.4.1.3 API Methods
where
K = 4.145 − 1.733 log (VSF − 145) The API-TDB [2] adopted methods developed by Riazi and
10
VSF = H 38(100) − H 99(210) Daubert for the estimation of the molecular weight of hydro-
H = 870 log [log (ν + 0.6)] + 154 carbon systems. In the 1982 edition of API-TDB, a modified
10
10
in which ν is the kinematic viscosity in cSt. This equation version of Eq. (2.38) was included, but in its latest editions
was developed some 60 years ago and requires kinematic (from 1987 to 1997) Eqs. (2.51) and (2.52) are included after
viscosities at 38 and 99 C in cSt as the only input param- recommendations made by the API-TDB Committee.
◦
eters. The Hirschler method was included in the API-TDB
in 1964 [2], but in the 1987 revision of API-TDB it was re- 2.4.1.4 Lee—Kesler Method
placed by Eq. (2.52). Riazi and Daubert [67] extensively com-
pared Eq. (2.52) with the Hirschler method and they found The molecular weight is related to boiling point and specific
that for some 160 fractions in the molecular weight range of gravity through an empirical relation as follows [13]:
200–800 the percent average absolute deviation (%AAD) for
these methods were 2.7% and 6.9%, respectively. Even if the M =−12272.6 + 9486.4SG + (8.3741 − 5.9917SG )T b
2
constants of the Hirschler correlation were reobtained from + (1 − 0.77084SG − 0.02058SG )
the data bank used for the evaluations, the accuracy of the (2.54) × (0.7465 − 222.466/T b )10 /T b
7
method improved only slightly from 6.9 to 6.1% [67]. 2
+ (1 − 0.80882SG + 0.02226SG )
12
Example 2.4—The viscosity and other properties of 5-n- × (0.3228 − 17.335/T b )10 /T b 3
butyldocosane, C 26 H 54 , as given in API RP-42 [18] are M =
366.7, SG = 0.8099, ν 38(100) = 11.44, and ν 99(210) = 3.02 cSt. High-molecular-weight data were also used in obtaining the
Calculate the molecular weight with %AD from the API constants. The correlation is recommended for use up to a
method, Eq. (2.52), and the Hirschler method (ASTM 2502), boiling point of about 750 K (∼850 F). Its evaluation is shown
◦
Eq. (2.53). in Section 2.9.
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT