Page 149 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 149
6.11. FLUIDIZATION OF BEDS OF PARTICLES WITH GASES 121
E
L
S
ET
ar
S
-2
m 50 om copper sh
600
Y
.
N E
3
C 625 pm copper shot
N
, 2 400
E
...
2 0 25 pm copper shot
2
d -
!! &
“,
Y
E m ”
i
m m
t! 2 200
a
z
03
I I I I
0.5 1 .o 1.5 2.0
Gas velocity, mls
Fluidizing rate, UIU,,
Ea1 b)
0 25
0 20
0 15
m‘
0 IO
o Wilhelmond KwoukZ2
0 05
001 002 003 004 00:
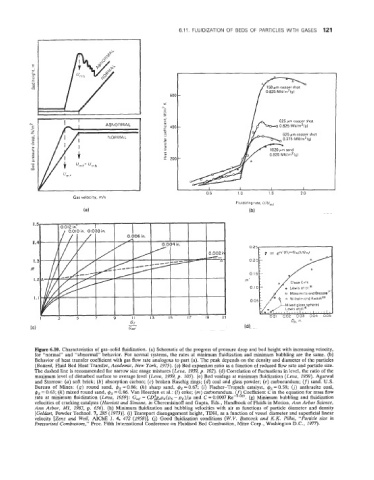
Fire 6.10. Characteristics of gas-solid fluidization. (a) Schematic of the progress of pressure drop and bed height with increasing velocity,
for “normal” and “abnormal” behavior. For normal systems, the rates at minimum fluidization and minimum bubbling are the same. (b)
Behavior of heat transfer coefficient with gas flow rate analogous to part (a). The peak depends on the density and diameter of the particles
(Botteril, Fluid Bed Heat Transfer, Academic, New York, 2975). (c) Bed expansion ratio as a function of reduced flow rate and particle size.
The dashed line is recommended for narrow size range mixtures (Leva, 2959, p. 202). (d) Correlation of fluctuations in level, the ratio of the
maximum level of disturbed surface to average level (Leva, 1959, p. 105). (e) Bed voidage at minimum fluidization (Leva, 1959). Aganval
and Storrow: (a) soft brick; (b) absorption carbon; (c) broken Raschig rings; (d) coal and glass powder; (e) carborundum; (f) sand. U.S.
Bureau of Mines: (g) round sand, & = 0.86; (h) sharp sand, 9, = 0.67; (i) Fischer-Tropsch catalyst, +s = 0.58; (j) anthracite coal,
GS = 0.63; (k) mixed round sand, #, = 0.86. Van Heerden et al.: (I) coke; (m) carborundum. (&hefficient C in the equation for mass flow
rate at minimum fluidization (Leva, 1959): Gmf = CD;g,p,(p, - pF)/p and C = 0.0007 Re- . (g) Minimum bubbling and fluidization
velocities of cracking catalysts (Harriotf and Simone, in Cheremisinoff and Gupta, Eds., Handbook of Fluids in Motion, Ann Arbor Science,
Ann Arbor, iW, 1983, p. 656). jh) Minimum fluidization and bubbling velocities with air as functions of particle diameter and density
[Geldart, Powder Technol. 7, 285 (197311. (i) Transport disengagement height, TDH, as a function of vessel diameter and superficial linear
velocity [Zenz and Weil, AIChE 1. 4, 472 (1958)l. (j) Good fluidization conditions (W.V. Batfcock and K.K. Pillai, “Particle size in
Pressurised Combustors,” Proc. Fifth International Conference on Fluidised Bed Combustion, Mitre Corp., Washington D.C., 1977).