Page 346 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 346
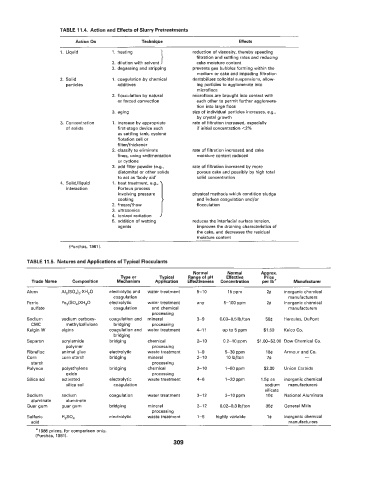
FABLE 11.4. Action and Effects of Slurry Pretreatments
I
Action On Technique Effects
-
1 filtration and settling rates and reducing
1. Liquid a. heating reduction of viscosity, thereby speeding
2. dilution with solvent cake moisture content
3. degassing and stripping prevents gas bubbles forming within the
medium or cake and impeding filtration
2. Solid 1. coagulation by chemical destabilizes colloidal suspensions, allow-
particles additives ing particles to agglomerate into
microflocs
2. flocculation by natural microflocs are brought into contact with
or forced convection each other to permit further agglornera-
tion into large flocs
3. aging size of individual particles increases, e.g.,
by crystal growth
3. Concentration 1. increase by appropriate rate of filtration increased, especially
of solids first-stage device such if initial concentration <2%
as settling tank, cyclone
flotation cell or
filter/thickener
2. classify to eliminate rate of filtration increased and cake
fines, using sedimentation moisture content reduced
or cyclone
3. add filter powder (e.g., rate of filtration increased by more
diatomite) or other solids porous cake and possibly by high total
to act as 'body aid' solid concentration
4. Solid/liquid 1. heat treatment, e.g.,
interaction Porteus process
involving pressure physical methods which condition sludge
cooking and induce coagulation and/or
2. freeze/thaw flocculation
3 ultrasonics
4 ionized radiation
5 addition of wetting reduces the interfacial surface tension,
agents improves the draining characteristics of
the cake, and decreases the residual
moisture content
(Purchas, 1981).
TABLE 11.5. Natures and Applications of Typical Flocculants
Normal Normal Approx.
Type or Typical Range of pH Effective Price
Trade Name Composition Mechanism Application Effectiveness Concentration per Ib" Manufacturer
Alum electrolytic and water treatment 5-10 15 PPm 2Q inorganic chemical
coagulation manufacturers
Ferric electrolytic water treatment any 5-100 ppm 2Q inorganic chemical
sulfate coagulation and chemical manufacturers
processing
Sodium :sodium carboxy- coagulation and mineral 3-9 0.03-0.5 Ib/ton Hercules, DuPont
CMC methylcellulose bridging processing
Kelgin W #algins coagulation and water treatment 4-1 1 up to 5 ppm $1.50 Kelco CO.
bridging
Separan acrylamide bridging chemical 2-10 0.2-10 ppm $1.00-$2.00 Dow Chemical Co.
polymer processing
Fibrefloc animal glue electrolytic waste treatment 1-9 5-30 ppm Armour and Co.
Corn corn starch bridging mineral 2-10 10 Ib/ton 7Q -
starch processing
Polynox polyethylene bridging chemical 2-10 1-50 ppm $2.00 Union Carbide
oxide processing
Silica SQI activated electrolytic waste treatment 4-6 1-20 ppm 1.5$ as inorganic chemical
silica sol coagulation sodium manufacturers
silicate
Sodium sodium coagulation water treatment 3-12 2-1 0 ppm 1 0e National Aluminate
aluminate aluminate
Guar gum guar gum bridging mineral 2-12 0.02-0.3 Ib/ton 35e General Milis
processing
Sulfuric H,SQ, electrolytic waste treatment 1-5 highly variable le inorganic chemical
acid manufacturers
"1966 prices, for comparison only.
(Purchas, 1981).
309