Page 121 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 121
Speight_Part II_A 11/7/01 3:16 PM Page 2.62
ANTIBIOTICS
The term antibiotic is broad and is defined as a substance produced by
microorganisms that has the capacity of inhibiting the growth of and even
of destroying other microorganisms by the action of very small amounts of
the substance.
Penicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, and cephalosporins are among
the most widely used. Synthetic modifications of the naturally occurring
antibiotic compounds have produced many variations that have the neces-
sary clinical properties.
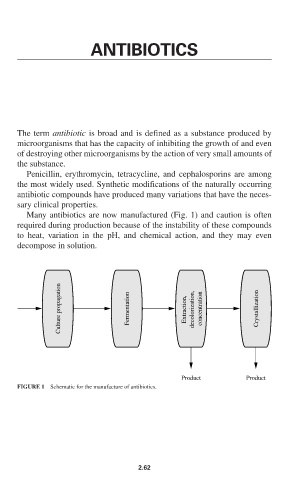
Many antibiotics are now manufactured (Fig. 1) and caution is often
required during production because of the instability of these compounds
to heat, variation in the pH, and chemical action, and they may even
decompose in solution.
Culture propagation Fermentation Extraction, decolorization, concentration Crystallization
Product Product
FIGURE 1 Schematic for the manufacture of antibiotics.
2.62