Page 183 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 183
Speight_Part II_C 11/7/01 3:08 PM Page 2.124
CALCIUM CARBONATE
Calcium carbonate (CaCO ) occurs naturally as calcite (density: 2.7), a
3
widely distributed mineral. Calcite is a common constituent of sedimen-
tary rocks, as a vein mineral, and as deposits from hot springs and in caves
as stalactites and stalagmites. Calcite is white or colorless through shades
of gray, red, yellow, green, blue, violet, brown, or even black when charged
with impurities; streaked, white; transparent to opaque. It may occasion-
ally show phosphorescence or fluorescence.
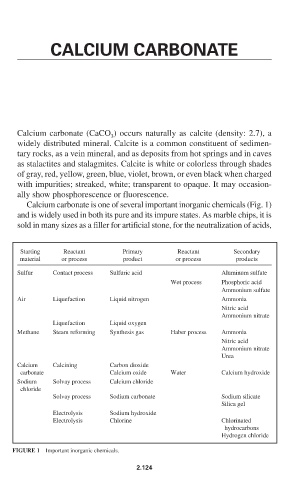
Calcium carbonate is one of several important inorganic chemicals (Fig. 1)
and is widely used in both its pure and its impure states. As marble chips, it is
sold in many sizes as a filler for artificial stone, for the neutralization of acids,
Starting Reactant Primary Reactant Secondary
material or process product or process products
Sulfur Contact process Sulfuric acid Aluminum sulfate
Wet process Phosphoric acid
Ammonium sulfate
Air Liquefaction Liquid nitrogen Ammonia
Nitric acid
Ammonium nitrate
Liquefaction Liquid oxygen
Methane Steam reforming Synthesis gas Haber process Ammonia
Nitric acid
Ammonium nitrate
Urea
Calcium Calcining Carbon dioxide
carbonate Calcium oxide Water Calcium hydroxide
Sodium Solvay process Calcium chloride
chloride
Solvay process Sodium carbonate Sodium silicate
Silica gel
Electrolysis Sodium hydroxide
Electrolysis Chlorine Chlorinated
hydrocarbons
Hydrogen chloride
FIGURE 1 Important inorganic chemicals.
2.124