Page 47 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 47
Speight_Part 1_N&O 11/7/01 3:02 PM Page 1.33
NITRATION 1.33
Water
Benzene
Nitric acid
Benzene
Washer
Nitrator Separator
Waste Distillation
water
treatment
Fresh Nitrobenzene
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid Water
reconcentration
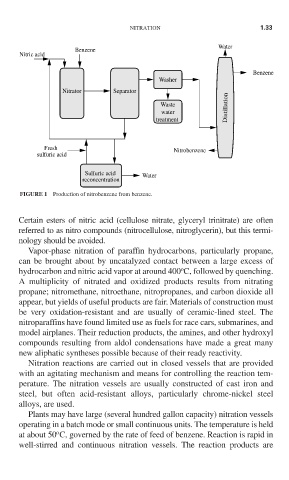
FIGURE 1 Production of nitrobenzene from benzene.
Certain esters of nitric acid (cellulose nitrate, glyceryl trinitrate) are often
referred to as nitro compounds (nitrocellulose, nitroglycerin), but this termi-
nology should be avoided.
Vapor-phase nitration of paraffin hydrocarbons, particularly propane,
can be brought about by uncatalyzed contact between a large excess of
o
hydrocarbon and nitric acid vapor at around 400 C, followed by quenching.
A multiplicity of nitrated and oxidized products results from nitrating
propane; nitromethane, nitroethane, nitropropanes, and carbon dioxide all
appear, but yields of useful products are fair. Materials of construction must
be very oxidation-resistant and are usually of ceramic-lined steel. The
nitroparaffins have found limited use as fuels for race cars, submarines, and
model airplanes. Their reduction products, the amines, and other hydroxyl
compounds resulting from aldol condensations have made a great many
new aliphatic syntheses possible because of their ready reactivity.
Nitration reactions are carried out in closed vessels that are provided
with an agitating mechanism and means for controlling the reaction tem-
perature. The nitration vessels are usually constructed of cast iron and
steel, but often acid-resistant alloys, particularly chrome-nickel steel
alloys, are used.
Plants may have large (several hundred gallon capacity) nitration vessels
operating in a batch mode or small continuous units. The temperature is held
o
at about 50 C, governed by the rate of feed of benzene. Reaction is rapid in
well-stirred and continuous nitration vessels. The reaction products are