Page 126 - Chemical engineering design
P. 126
106
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
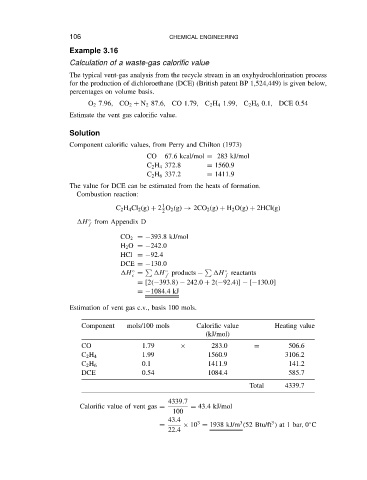
Example 3.16
Calculation of a waste-gas calorific value
The typical vent-gas analysis from the recycle stream in an oxyhydrochlorination process
for the production of dichloroethane (DCE) (British patent BP 1,524,449) is given below,
percentages on volume basis.
O 2 7.96, CO 2 C N 2 87.6, CO 1.79, C 2 H 4 1.99, C 2 H 6 0.1, DCE 0.54
Estimate the vent gas calorific value.
Solution
Component calorific values, from Perry and Chilton (1973)
CO 67.6 kcal/mol D 283 kJ/mol
C 2 H 4 372.8 D 1560.9
C 2 H 6 337.2 D 1411.9
The value for DCE can be estimated from the heats of formation.
Combustion reaction:
1
C 2 H 4 Cl 2 (g) C 2 O 2 (g) ! 2CO 2 (g) C H 2 O(g) C 2HCl(g)
2
Ž
H from Appendix D
f
CO 2 D 393.8kJ/mol
H 2 O D 242.0
HCl D 92.4
DCE D 130.0
Ž
Ž
Ž
H D H products H reactants
c f f
D [2 393.8 242.0 C 2 92.4 ] [ 130.0]
D 1084.4kJ
Estimation of vent gas c.v., basis 100 mols.
Component mols/100 mols Calorific value Heating value
(kJ/mol)
CO 1.79 ð 283.0 D 506.6
1.99 1560.9 3106.2
C 2 H 4
0.1 1411.9 141.2
C 2 H 6
DCE 0.54 1084.4 585.7
Total 4339.7
4339.7
Calorific value of vent gas D D 43.4kJ/mol
100
43.4
3
3
3
Ž
D ð 10 D 1938 kJ/m 52 Btu/ft at 1 bar, 0 C
22.4