Page 127 - Chemical engineering design
P. 127
107
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES
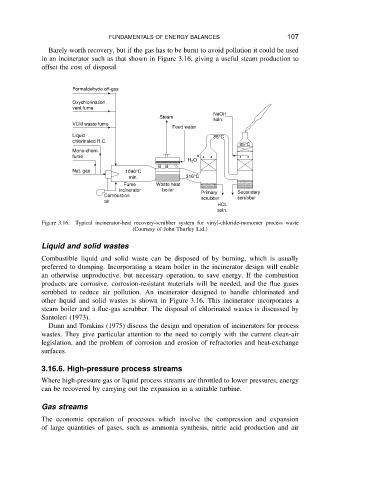
Barely worth recovery, but if the gas has to be burnt to avoid pollution it could be used
in an incinerator such as that shown in Figure 3.16, giving a useful steam production to
offset the cost of disposal.
Formaldehyde off-gas
Oxychlorination
vent fume
NaOH
Steam
soln.
VCM waste fume
Feed water
Liquid 88°C
chlorinated H.C.
85°C
Mono-chem.
fume
H 2 O
Nat. gas 1090°C
min. 316°C
Fume Waste heat
incinerator boiler Secondary
Combustion Primary scrubber
scrubber
air
HCL
soln.
Figure 3.16. Typical incinerator-heat recovery-scrubber system for vinyl-chloride-monomer process waste
(Courtesy of John Thurley Ltd.)
Liquid and solid wastes
Combustible liquid and solid waste can be disposed of by burning, which is usually
preferred to dumping. Incorporating a steam boiler in the incinerator design will enable
an otherwise unproductive, but necessary operation, to save energy. If the combustion
products are corrosive, corrosion-resistant materials will be needed, and the flue gases
scrubbed to reduce air pollution. An incinerator designed to handle chlorinated and
other liquid and solid wastes is shown in Figure 3.16. This incinerator incorporates a
steam boiler and a flue-gas scrubber. The disposal of chlorinated wastes is discussed by
Santoleri (1973).
Dunn and Tomkins (1975) discuss the design and operation of incinerators for process
wastes. They give particular attention to the need to comply with the current clean-air
legislation, and the problem of corrosion and erosion of refractories and heat-exchange
surfaces.
3.16.6. High-pressure process streams
Where high-pressure gas or liquid process streams are throttled to lower pressures, energy
can be recovered by carrying out the expansion in a suitable turbine.
Gas streams
The economic operation of processes which involve the compression and expansion
of large quantities of gases, such as ammonia synthesis, nitric acid production and air