Page 169 - Chemical engineering design
P. 169
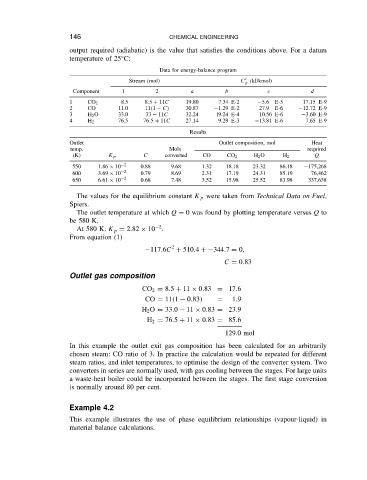
146
output required (adiabatic) is the value that satisfies the conditions above. For a datum
Ž
temperature of 25 C: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Data for energy-balance program
Stream (mol) C ° (kJ/kmol)
p
Component 1 2 a b c d
1 CO 2 8.5 8.5 C 11C 19.80 7.34 E-2 5.6 E-5 17.15 E-9
2 CO 11.0 11 1 C 30.87 1.29 E-2 27.9 E-6 12.72 E-9
3 H 2 O 33.0 33 11C 32.24 l9.24 E-4 10.56 E-6 3.60 E-9
4 H 2 76.5 76.5 C 11C 27.14 9.29 E-3 13.81 E-6 7.65 E-9
Results
Outlet Outlet composition, mol Heat
temp. Mols required
(K) K p C converted CO CO 2 H 2 O H 2 Q
550 1.86 ð 10 2 0.88 9.68 1.32 18.18 23.32 86.18 175,268
600 3.69 ð 10 2 0.79 8.69 2.31 17.19 24.31 85.19 76,462
650 6.61 ð 10 2 0.68 7.48 3.52 15.98 25.52 83.98 337,638
The values for the equilibrium constant K p were taken from Technical Data on Fuel,
Spiers.
The outlet temperature at which Q D 0 was found by plotting temperature versus Q to
be 580 K.
2
At 580 K, K p D 2.82 ð 10 .
From equation (1)
2
117.6C C 510.4 C 344.7 D 0,
C D 0.83
Outlet gas composition
CO 2 D 8.5 C 11 ð 0.83 D 17.6
CO D 11 1 0.83 D 1.9
H 2 O D 33.0 11 ð 0.83 D 23.9
H 2 D 76.5 C 11 ð 0.83 D 85.6
129.0 mol
In this example the outlet exit gas composition has been calculated for an arbitrarily
chosen steam: CO ratio of 3. In practice the calculation would be repeated for different
steam ratios, and inlet temperatures, to optimise the design of the converter system. Two
converters in series are normally used, with gas cooling between the stages. For large units
a waste-heat boiler could be incorporated between the stages. The first stage conversion
is normally around 80 per cent.
Example 4.2
This example illustrates the use of phase equilibrium relationships (vapour-liquid) in
material balance calculations.