Page 342 - Chemical engineering design
P. 342
DESIGN INFORMATION AND DATA
N
C
Cl
Br
I
O
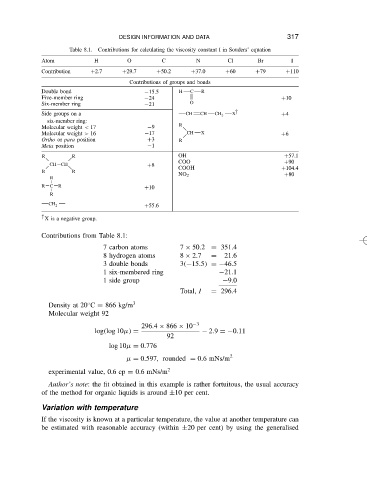
Atom Table 8.1. H Contributions for calculating the viscosity constant I in Souders’ equation 317
Contribution C2.7 C29.7 C50.2 C37.0 C60 C79 C110
Contributions of groups and bonds
Double bond 15.5 H C R
Five-member ring 24 C10
Six-member ring 21 O
†
Side groups on a CH CH CH 2 X C4
six-member ring:
Molecular weight < 17 9 R
Molecular weight > 16 17 CH X C6
Ortho or para position C3 R
Meta position 1
R R OH C57.1
COO C90
CH CH C8
COOH C104.4
R R
NO 2 C80
R
R C R C10
R
C55.6
CH 2
† X is a negative group.
Contributions from Table 8.1:
7 carbon atoms 7 ð 50.2 D 351.4
8 hydrogen atoms 8 ð 2.7 D 21.6
3 double bonds 3 15.5 D 46.5
1 six-membered ring 21.1
1 side group 9.0
Total, I D 296.4
Ž
Density at 20 C D 866 kg/m 3
Molecular weight 92
296.4 ð 866 ð 10 3
log log 10 D 2.9 D 0.11
92
log 10 D 0.776
D 0.597, rounded D 0.6mNs/m 2
experimental value, 0.6 cp D 0.6 mNs/m 2
Author’s note: the fit obtained in this example is rather fortuitous, the usual accuracy
of the method for organic liquids is around š10 per cent.
Variation with temperature
If the viscosity is known at a particular temperature, the value at another temperature can
be estimated with reasonable accuracy (within š20 per cent) by using the generalised