Page 111 - Chemical equilibria Volume 4
P. 111
r
Molecular Chemical Equiilibria 87
n
a
3.3.2.10. Ellingham diagram and solutions solids
m
h
d
e
t
In the case where the solids involved in the reaction belong to solid
f
p
x
v
n
solutions, their activities play a part in the expression of the affinity which is
u
e
r
cancelled out at equilibrium, for a metal oxide MO, in accordance wiith:
c
d
⎛ P a (I) ⎞ ⎞
Δ g +
M
A = A
T
A 0 − RT lnQ (I) =−Δ r 0 Rln ⎜ O 0 2 x (I) ⎟ ⎟ = 0 [3.63]
T
⎝ P a MO ⎠ ⎠
At equilibrium, we obtain the expression of the standard Gibbs ennergy:
a
q
w
e
⎛ P a (I) ⎞ ⎞
Δ Δ g = Rln ⎜ O 0 2 × M [3.64]
0
T
n
(I) ⎟
r
⎝ P a MO ⎠ ⎠
a
s
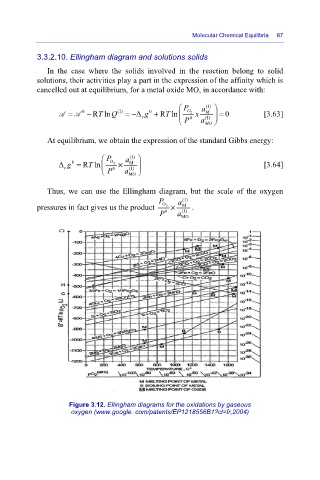
Thus, we can use the Ellingham diagram, but the scale of thee oxygen
s
g
P a (I)
o
e
v
pressures in fact gives us the product O 2 × M .
(I)
P 0 a a MO
d
Figure 3.12. Ellingham diagrams for the oxidations by gaseous
h
2
?
w
o
oxygen (www.google. com/patents/EP1218556B1?cl=fr,2004)
P