Page 278 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 278
Compressors, Pumps, and Turbines 257
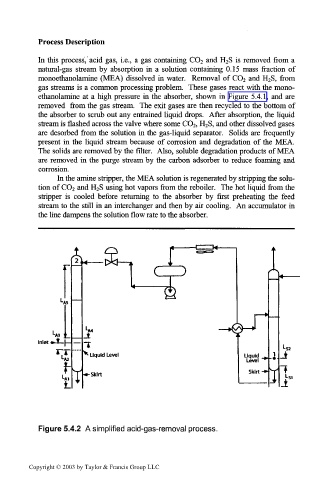
Process Description
In this process, acid gas, i.e., a gas containing CO 2 and H 2S is removed from a
natural-gas stream by absorption in a solution containing 0.15 mass fraction of
monoethanolamine (MEA) dissolved in water. Removal of CO 2 and H 2S, from
gas streams is a common processing problem. These gases react with the mono-
ethanolamine at a high pressure in the absorber, shown in Figure 5.4.1, and are
removed from the gas stream. The exit gases are then recycled to the bottom of
the absorber to scrub out any entrained liquid drops. After absorption, the liquid
stream is flashed across the valve where some CO 2, H 2S, and other dissolved gases
are desorbed from the solution in the gas-liquid separator. Solids are frequently
present in the liquid stream because of corrosion and degradation of the MEA.
The solids are removed by the filter. Also, soluble degradation products of MEA
are removed in the purge stream by the carbon adsorber to reduce foaming and
corrosion.
In the amine stripper, the MEA solution is regenerated by stripping the solu-
tion of CO 2 and H 2S using hot vapors from the reboiler. The hot liquid from the
stripper is cooled before returning to the absorber by first preheating the feed
stream to the still in an interchanger and then by air cooling. An accumulator in
the line dampens the solution flow rate to the absorber.
A
Inlet *-*-[- —
Figure 5.4.2 A simplified acid-gas-removal process.
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC