Page 81 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 81
66 Chapter 2
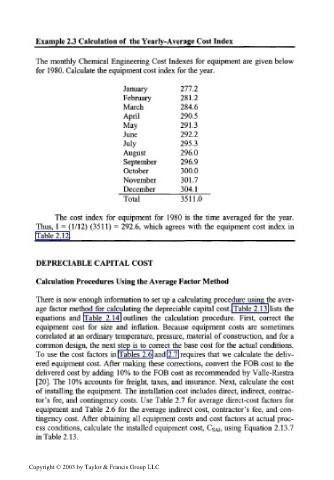
Example 2.3 Calculation of the Yearly-Average Cost Index__________
The monthly Chemical Engineering Cost Indexes for equipment are given below
for 1980. Calculate the equipment cost index for the year.
January 277.2
February 281.2
March 284.6
April 290.5
May 291.3
June 292.2
July 295.3
August 296.0
September 296.9
October 300.0
November 301.7
December 304.1
Total 3511.0
The cost index for equipment for 1980 is the time averaged for the year.
Thus, I = (1/12) (3511) = 292.6, which agrees with the equipment cost index in
Table 2.12.
DEPRECIABLE CAPITAL COST
Calculation Procedures Using the Average Factor Method
There is now enough information to set up a calculating procedure using the aver-
age factor method for calculating the depreciable capital cost. Table 2.13 lists the
equations and Table 2.14 outlines the calculation procedure. First, correct the
equipment cost for size and inflation. Because equipment costs are sometimes
correlated at an ordinary temperature, pressure, material of construction, and for a
common design, the next step is to correct the base cost for the actual conditions.
To use the cost factors in Tables 2.6 and 2.7 requires that we calculate the deliv-
ered equipment cost. After making these corrections, convert the FOB cost to the
delivered cost by adding 10% to the FOB cost as recommended by Valle-Riestra
[20]. The 10% accounts for freight, taxes, and insurance. Next, calculate the cost
of installing the equipment. The installation cost includes direct, indirect, contrac-
tor's fee, and contingency costs. Use Table 2.7 for average direct-cost factors for
equipment and Table 2.6 for the average indirect cost, contractor's fee, and con-
tingency cost. After obtaining all equipment costs and cost factors at actual proc-
ess conditions, calculate the installed equipment cost, Ci, using Equation 2.13.7
SA
in Table 2.13.
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC