Page 229 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 229
8.3 Nonchromatographic Separation Process Description 207
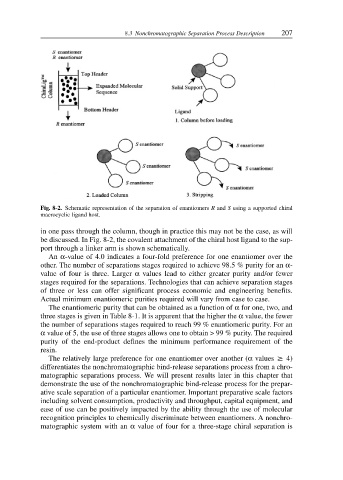
Fig. 8-2. Schematic representation of the separation of enantiomers R and S using a supported chiral
macrocyclic ligand host.
in one pass through the column, though in practice this may not be the case, as will
be discussed. In Fig. 8-2, the covalent attachment of the chiral host ligand to the sup-
port through a linker arm is shown schematically.
An α-value of 4.0 indicates a four-fold preference for one enantiomer over the
other. The number of separations stages required to achieve 98.5 % purity for an α-
value of four is three. Larger α values lead to either greater purity and/or fewer
stages required for the separations. Technologies that can achieve separation stages
of three or less can offer significant process economic and engineering benefits.
Actual minimum enantiomeric purities required will vary from case to case.
The enantiomeric purity that can be obtained as a function of α for one, two, and
three stages is given in Table 8-1. It is apparent that the higher the α value, the fewer
the number of separations stages required to reach 99 % enantiomeric purity. For an
α value of 5, the use of three stages allows one to obtain > 99 % purity. The required
purity of the end-product defines the minimum performance requirement of the
resin.
The relatively large preference for one enantiomer over another (α values 6 4)
differentiates the nonchromatographic bind-release separations process from a chro-
matographic separations process. We will present results later in this chapter that
demonstrate the use of the nonchromatographic bind-release process for the prepar-
ative scale separation of a particular enantiomer. Important preparative scale factors
including solvent consumption, productivity and throughput, capital equipment, and
ease of use can be positively impacted by the ability through the use of molecular
recognition principles to chemically discriminate between enantiomers. A nonchro-
matographic system with an α value of four for a three-stage chiral separation is