Page 257 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 257
9.5 The Steady State TMB Model 235
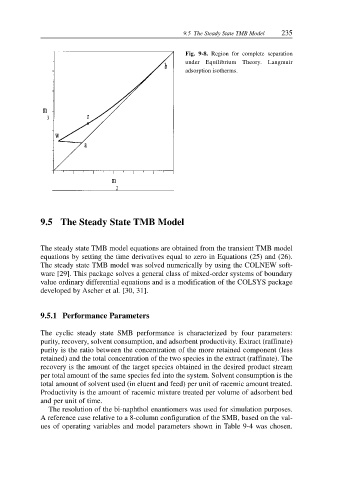
Fig. 9-8. Region for complete separation
under Equilibrium Theory. Langmuir
adsorption isotherms.
9.5 The Steady State TMB Model
The steady state TMB model equations are obtained from the transient TMB model
equations by setting the time derivatives equal to zero in Equations (25) and (26).
The steady state TMB model was solved numerically by using the COLNEW soft-
ware [29]. This package solves a general class of mixed-order systems of boundary
value ordinary differential equations and is a modification of the COLSYS package
developed by Ascher et al. [30, 31].
9.5.1 Performance Parameters
The cyclic steady state SMB performance is characterized by four parameters:
purity, recovery, solvent consumption, and adsorbent productivity. Extract (raffinate)
purity is the ratio between the concentration of the more retained component (less
retained) and the total concentration of the two species in the extract (raffinate). The
recovery is the amount of the target species obtained in the desired product stream
per total amount of the same species fed into the system. Solvent consumption is the
total amount of solvent used (in eluent and feed) per unit of racemic amount treated.
Productivity is the amount of racemic mixture treated per volume of adsorbent bed
and per unit of time.
The resolution of the bi-naphthol enantiomers was used for simulation purposes.
A reference case relative to a 8-column configuration of the SMB, based on the val-
ues of operating variables and model parameters shown in Table 9-4 was chosen.