Page 112 - Circuit Analysis II with MATLAB Applications
P. 112
Chapter 3 Elementary Signals
ft G' t – a = fa G' t – a – f ' a G t – a
Then, for this example,
2 2 d 2
t G' t – 3 = t G' t – 3 – -----t G t – 3
t = 3 dt t = 3
=
9G' t – 3 6G t – 3
–
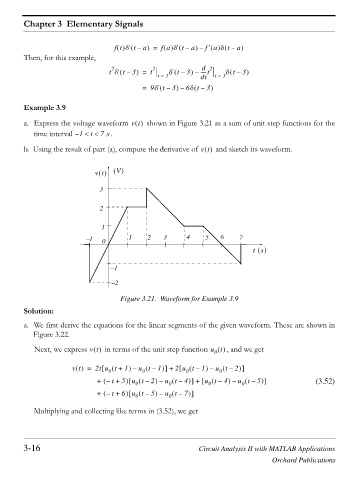
Example 3.9
a. Express the voltage waveform vt shown in Figure 3.21 as a sum of unit step functions for the
time interval 1 – t 7 . s
b. Using the result of part (a), compute the derivative of vt and sketch its waveform.
V
vt
3
2
1
1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
ts
1
2
Figure 3.21. Waveform for Example 3.9
Solution:
a. We first derive the equations for the linear segments of the given waveform. These are shown in
Figure 3.22.
Next, we express vt in terms of the unit step function u t , and we get
0
vt = 2t u t + > 0 1 – u t – 1 @ 2u t – 1 – u t – 2 @
+
>
0
0
0
t
+ – + 5 u t – > 0 2 – u t – 4 @ + u t – 4 – u t – 5 @ (3.52)
>
0
0
0
t
+ – + 6 u t – > 0 5 – u t – 7 @
0
Multiplying and collecting like terms in (3.52), we get
3-16 Circuit Analysis II with MATLAB Applications
Orchard Publications