Page 152 - Civil Engineering Formulas
P. 152
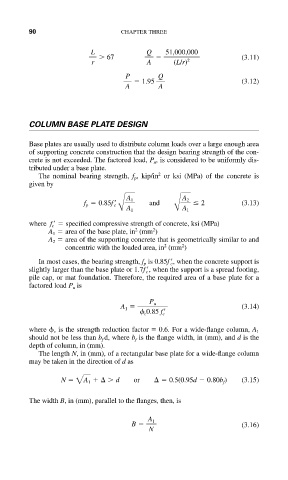
90 CHAPTER THREE
L Q 51,000,000
67 (3.11)
r A (L/r) 2
P Q
1.95 (3.12)
A A
COLUMN BASE PLATE DESIGN
Base plates are usually used to distribute column loads over a large enough area
of supporting concrete construction that the design bearing strength of the con-
crete is not exceeded. The factored load, P u , is considered to be uniformly dis-
tributed under a base plate.
2
The nominal bearing strength, f p , kip/in or ksi (MPa) of the concrete is
given by
and
A 1 A 2
f p 0.85f c 2 (3.13)
B A 1 B A 1
where f c specified compressive strength of concrete, ksi (MPa)
2
2
A 1 area of the base plate, in (mm )
A 2 area of the supporting concrete that is geometrically similar to and
2
2
concentric with the loaded area, in (mm )
, when the concrete support is
In most cases, the bearing strength, f p is 0.85f c
, when the support is a spread footing,
slightly larger than the base plate or 1.7f c
pile cap, or mat foundation. Therefore, the required area of a base plate for a
factored load P u is
A 1 P u (3.14)
c 0.85 f c
where c is the strength reduction factor 0.6. For a wide-flange column, A 1
should not be less than b f d, where b f is the flange width, in (mm), and d is the
depth of column, in (mm).
The length N, in (mm), of a rectangular base plate for a wide-flange column
may be taken in the direction of d as
N 2 A 1 d or 0.5(0.95d 0.80b f ) (3.15)
The width B, in (mm), parallel to the flanges, then, is
B A 1 (3.16)
N