Page 85 - Classification Parameter Estimation & State Estimation An Engg Approach Using MATLAB
P. 85
74 PARAMETER ESTIMATION
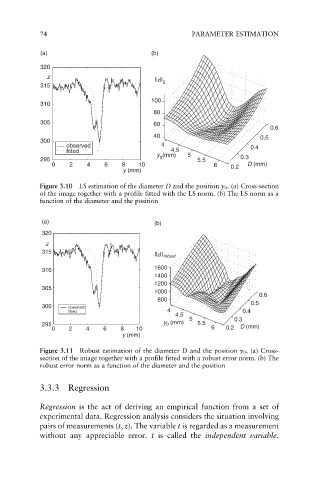
(a) (b)
320
z
||ε||
315 2
100
310
80
305 60
0.6
40 0.5
300
observed 4 0.4
fitted 4.5
y (mm) 5
295 0 5.5 0.3
0 2 4 6 8 10 6 0.2 D (mm)
y (mm)
Figure 3.10 LS estimation of the diameter D and the position y 0 . (a) Cross-section
of the image together with a profile fitted with the LS norm. (b) The LS norm as a
function of the diameter and the position
(a) (b)
320
z
315
||ε|| robust
310 1600
1400
1200
305
1000
0.6
800
300 observed 0.5
fitted 4 0.4
4.5
5 0.3
295 y 0 (mm) 5.5
0 2 4 6 8 10 6 0.2 D (mm)
y (mm)
Figure 3.11 Robust estimation of the diameter D and the position y 0 . (a) Cross-
section of the image together with a profile fitted with a robust error norm. (b) The
robust error norm as a function of the diameter and the position
3.3.3 Regression
Regression is the act of deriving an empirical function from a set of
experimental data. Regression analysis considers the situation involving
pairs of measurements (t, z). The variable t is regarded as a measurement
without any appreciable error. t is called the independent variable.