Page 265 - Classification Parameter Estimation & State Estimation An Engg Approach Using MATLAB
P. 265
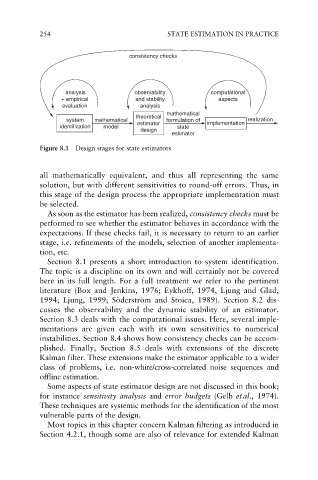
254 STATE ESTIMATION IN PRACTICE
consistency checks
analysis observability computational
+ empirical and stability aspects
evaluation analysis
mathematical
theoretical
system mathematical formulation of realization
identification model estimator state implementation
design
estimator
Figure 8.1 Design stages for state estimators
all mathematically equivalent, and thus all representing the same
solution, but with different sensitivities to round-off errors. Thus, in
this stage of the design process the appropriate implementation must
be selected.
As soon as the estimator has been realized, consistency checks must be
performed to see whether the estimator behaves in accordance with the
expectations. If these checks fail, it is necessary to return to an earlier
stage, i.e. refinements of the models, selection of another implementa-
tion, etc.
Section 8.1 presents a short introduction to system identification.
The topic is a discipline on its own and will certainly not be covered
here in its full length. For a full treatment we refer to the pertinent
literature (Box and Jenkins, 1976; Eykhoff, 1974, Ljung and Glad,
1994; Ljung, 1999; Soderstrom and Stoica, 1989). Section 8.2 dis-
¨
¨
cusses the observability and the dynamic stability of an estimator.
Section 8.3 deals with the computational issues. Here, several imple-
mentations are given each with its own sensitivities to numerical
instabilities. Section 8.4 shows how consistency checks can be accom-
plished. Finally, Section 8.5 deals with extensions of the discrete
Kalman filter. These extensions make the estimator applicable to a wider
class of problems, i.e. non-white/cross-correlated noise sequences and
offline estimation.
Some aspects of state estimator design are not discussed in this book;
for instance sensitivity analysis and error budgets (Gelb et al., 1974).
These techniques are systemic methods for the identification of the most
vulnerable parts of the design.
Most topics in this chapter concern Kalman filtering as introduced in
Section 4.2.1, though some are also of relevance for extended Kalman