Page 147 - Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
P. 147
138 Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
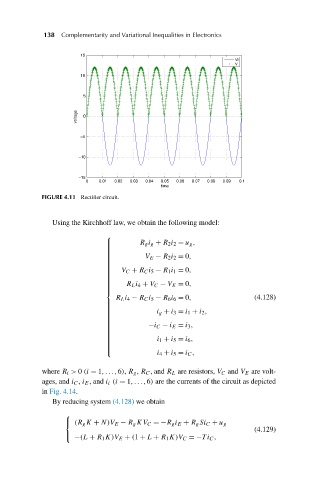
FIGURE 4.11 Rectifier circuit.
Using the Kirchhoff law, we obtain the following model:
⎧
R g i g + R 2 i 2 = u g ,
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
V E − R 2 i 2 = 0,
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪ V C + R C i 5 − R 1 i 1 = 0,
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪ R L i 4 + V C − V E = 0,
⎪
⎪
⎨
R L i 4 − R C i 5 − R 6 i 6 = 0, (4.128)
⎪
⎪
i g + i 3 = i 1 + i 2 ,
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
−i C − i E = i 3 ,
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
i 1 + i 5 = i 6 ,
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
i 4 + i 5 = i C ,
⎩
where R i > 0 (i = 1,...,6), R g , R C , and R L are resistors, V C and V E are volt-
ages, and i C , i E , and i i (i = 1,...,6) are the currents of the circuit as depicted
in Fig. 4.14.
By reducing system (4.128) we obtain
⎧
⎨ (R g K + N)V E − R g KV C =−R g i E + R g Si C + u g
(4.129)
−(L + R 1 K)V E + (1 + L + R 1 K)V C =−Ti C ,
⎩