Page 159 - Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
P. 159
150 Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
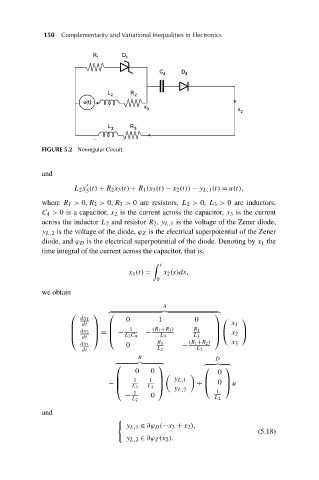
FIGURE 5.2 Nonregular Circuit.
and
L 2 x (t) + R 2 x 3 (t) + R 1 (x 3 (t) − x 2 (t)) − y L,1 (t) = u(t),
3
where R 1 > 0,R 2 > 0,R 3 > 0 are resistors, L 2 > 0, L 3 > 0 are inductors,
C 4 > 0 is a capacitor, x 2 is the current across the capacitor, x 3 is the current
across the inductor L 2 and resistor R 2 , y L,1 is the voltage of the Zener diode,
y L,2 is the voltage of the diode, ϕ Z is the electrical superpotential of the Zener
diode, and ϕ D is the electrical superpotential of the diode. Denoting by x 1 the
time integral of the current across the capacitor, that is,
t
x 1 (t) = x 2 (s)ds,
0
we obtain
A
⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞
dx 1 0 1 0 ⎛ ⎞
dt x 1
1 R 1
⎜ ⎟ ⎜ (R 1 +R 3 ) ⎟
⎜ dx 2 ⎟ = ⎜ − − ⎟⎝ x 2 ⎠
L 3 C 4 L 3 L 3
⎝ ⎝ ⎠
dt ⎠
dx 3 0 R 1 − (R 1 +R 2 ) x 3
dt L 2 L 2
B D
⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞
0 0 0
⎜ 1 1 ⎟ y L,1
⎟
− ⎜ ⎟ ⎜ 0 ⎠ u
L 3 + ⎝
⎝ L 3 ⎠ y L,2
1 1
− 0
L 2 L 2
and
y L,1 ∈ ∂ϕ D (−x 3 + x 2 ),
(5.18)
y L,2 ∈ ∂ϕ Z (x 2 ).