Page 39 - Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
P. 39
The Convex Subdifferential Relation Chapter | 2 29
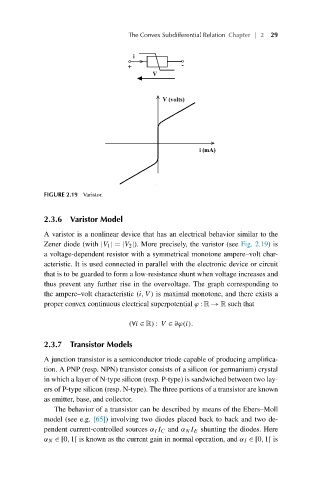
FIGURE 2.19 Varistor.
2.3.6 Varistor Model
A varistor is a nonlinear device that has an electrical behavior similar to the
Zener diode (with |V 1 |=|V 2 |). More precisely, the varistor (see Fig. 2.19)is
a voltage-dependent resistor with a symmetrical monotone ampere–volt char-
acteristic. It is used connected in parallel with the electronic device or circuit
that is to be guarded to form a low-resistance shunt when voltage increases and
thus prevent any further rise in the overvoltage. The graph corresponding to
the ampere–volt characteristic (i,V ) is maximal monotone, and there exists a
proper convex continuous electrical superpotential ϕ : R → R such that
(∀i ∈ R) : V ∈ ∂ϕ(i).
2.3.7 Transistor Models
A junction transistor is a semiconductor triode capable of producing amplifica-
tion. A PNP (resp. NPN) transistor consists of a silicon (or germanium) crystal
in which a layer of N-type silicon (resp. P-type) is sandwiched between two lay-
ers of P-type silicon (resp. N-type). The three portions of a transistor are known
as emitter, base, and collector.
The behavior of a transistor can be described by means of the Ebers–Moll
model (see e.g. [65]) involving two diodes placed back to back and two de-
pendent current-controlled sources α I I C and α N I E shunting the diodes. Here
α N ∈[0,1[ is known as the current gain in normal operation, and α I ∈[0,1[ is