Page 34 - Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
P. 34
24 Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
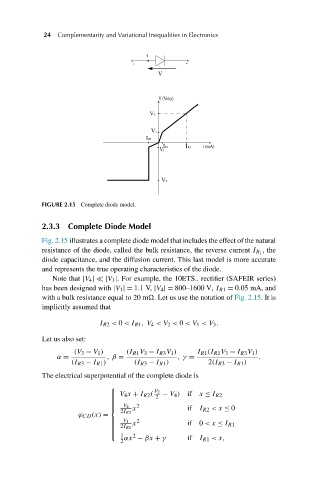
FIGURE 2.15 Complete diode model.
2.3.3 Complete Diode Model
Fig. 2.15 illustrates a complete diode model that includes the effect of the natural
,the
resistance of the diode, called the bulk resistance, the reverse current I R 1
diode capacitance, and the diffusion current. This last model is more accurate
and represents the true operating characteristics of the diode.
Note that |V 4 | |V 1 |. For example, the 10ETS.. rectifier (SAFEIR series)
has been designed with |V 1 |= 1.1V, |V 4 |= 800–1600 V, I R1 = 0.05 mA, and
with a bulk resistance equal to 20 m . Let us use the notation of Fig. 2.15.Itis
implicitly assumed that
I R2 < 0 <I R1 ,V 4 <V 2 < 0 <V 1 <V 3 .
Let us also set:
(V 3 − V 1 ) (I R1 V 3 − I R3 V 1 ) I R1 (I R1 V 3 − I R3 V 1 )
α = ,β = ,γ = .
(I R3 − I R1 ) (I R3 − I R1 ) 2(I R3 − I R1 )
The electrical superpotential of the complete diode is
⎧
⎪ V 4 x + I R2 ( V 2 − V 4 ) if
2 x ≤ I R2
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪ V 2 2
⎨ x if I R2 <x ≤ 0
2I R2
ϕ CD (x) =
⎪ V 1 2
⎪ x if 0 <x ≤ I R1
⎪ 2I R1
⎪
⎪
⎪
2
⎩ 1 αx − βx + γ if I R1 <x,
2