Page 57 - Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
P. 57
48 Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
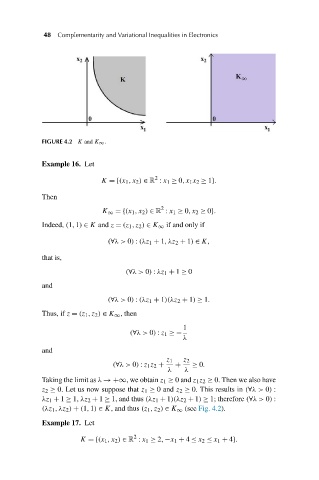
FIGURE 4.2 K and K ∞ .
Example 16. Let
2
K ={(x 1 ,x 2 ) ∈ R : x 1 ≥ 0,x 1 x 2 ≥ 1}.
Then
2
K ∞ ={(x 1 ,x 2 ) ∈ R : x 1 ≥ 0,x 2 ≥ 0}.
Indeed, (1,1) ∈ K and z = (z 1 ,z 2 ) ∈ K ∞ if and only if
(∀λ> 0) : (λz 1 + 1,λz 2 + 1) ∈ K,
that is,
(∀λ> 0) : λz 1 + 1 ≥ 0
and
(∀λ> 0) : (λz 1 + 1)(λz 2 + 1) ≥ 1.
Thus, if z = (z 1 ,z 2 ) ∈ K ∞ , then
1
(∀λ> 0) : z 1 ≥−
λ
and
z 1 z 2
(∀λ> 0) : z 1 z 2 + + ≥ 0.
λ λ
Taking the limit as λ →+∞, we obtain z 1 ≥ 0 and z 1 z 2 ≥ 0. Then we also have
z 2 ≥ 0. Let us now suppose that z 1 ≥ 0 and z 2 ≥ 0. This results in (∀λ> 0) :
λz 1 + 1 ≥ 1, λz 2 + 1 ≥ 1, and thus (λz 1 + 1)(λz 2 + 1) ≥ 1; therefore (∀λ> 0) :
(λz 1 ,λz 2 ) + (1,1) ∈ K, and thus (z 1 ,z 2 ) ∈ K ∞ (see Fig. 4.2).
Example 17. Let
2
K ={(x 1 ,x 2 ) ∈ R : x 1 ≥ 2,−x 1 + 4 ≤ x 2 ≤ x 1 + 4}.