Page 62 - Complementarity and Variational Inequalities in Electronics
P. 62
A Variational Inequality Theory Chapter | 4 53
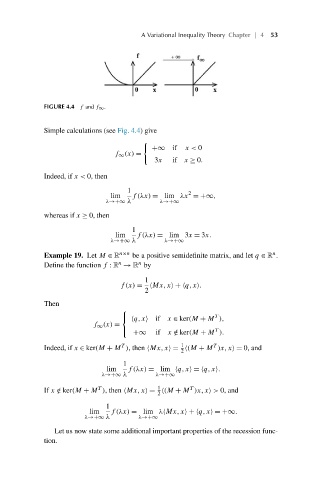
FIGURE 4.4 f and f ∞ .
Simple calculations (see Fig. 4.4)give
+∞ if x< 0
f ∞ (x) =
3x if x ≥ 0.
Indeed, if x< 0, then
1 2
lim f(λx) = lim λx =+∞,
λ→+∞ λ λ→+∞
whereas if x ≥ 0, then
1
lim f(λx) = lim 3x = 3x.
λ→+∞ λ λ→+∞
n
Example 19. Let M ∈ R n×n be a positive semidefinite matrix, and let q ∈ R .
n
n
Define the function f : R → R by
1
f(x) = Mx,x + q,x .
2
Then
⎧
q,x if x ∈ ker(M + M ),
⎨ T
f ∞ (x) =
T
+∞
⎩ if x/∈ ker(M + M ).
1
T
T
Indeed, if x ∈ ker(M + M ), then Mx,x = (M + M )x,x = 0, and
2
1
lim f(λx) = lim q,x = q,x .
λ→+∞ λ λ→+∞
1
T
T
If x/∈ ker(M + M ), then Mx,x = (M + M )x,x > 0, and
2
1
lim f(λx) = lim λ Mx,x + q,x =+∞.
λ→+∞ λ λ→+∞
Let us now state some additional important properties of the recession func-
tion.