Page 77 - Complete Wireless Design
P. 77
Modulation
76 Chapter Two
gle CW frequency sources, but possess phase noise. Since digital signals carry
their information in the phase of the signal, this insertion of phase variances
will create increased BER, with the density of the modulation affecting the
severity of the BER degradation: The higher-order QAM constellations, such
as QAM-256, can be severely degraded at relatively small levels of phase
noise. This is because their constellation points are so densely packed, causing
their phase/amplitude points to bisect digital decision boundaries.
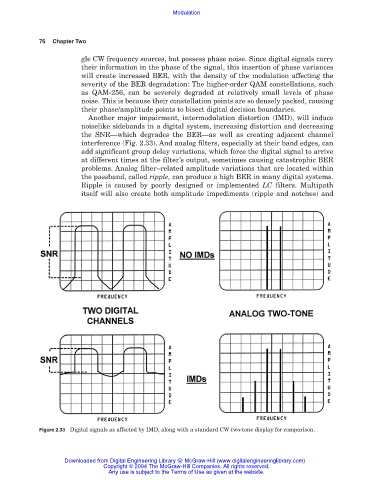
Another major impairment, intermodulation distortion (IMD), will induce
noiselike sidebands in a digital system, increasing distortion and decreasing
the SNR—which degrades the BER—as well as creating adjacent channel
interference (Fig. 2.33). And analog filters, especially at their band edges, can
add significant group delay variations, which force the digital signal to arrive
at different times at the filter’s output, sometimes causing catastrophic BER
problems. Analog filter–related amplitude variations that are located within
the passband, called ripple, can produce a high BER in many digital systems.
Ripple is caused by poorly designed or implemented LC filters. Multipath
itself will also create both amplitude impediments (ripple and notches) and
Figure 2.33 Digital signals as affected by IMD, along with a standard CW two-tone display for comparison.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.