Page 142 - Computational Fluid Dynamics for Engineers
P. 142
128 4. Numerical Methods for Model Parabolic and Elliptic Equations
y
fth " a
}>N
yj
Xi Xtf
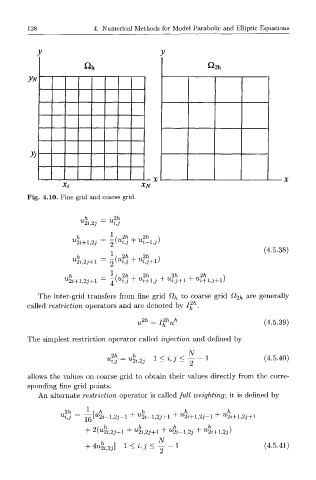
Fig. 4.10. Fine grid and coarse grid.
u U
2i,2j ~ hj
u % u
2i+l,2j — 2^ ^ t+lj)
(4.5.38)
2h
i, h - -(v 2h + v . A
u
2i,2j+l — o V ^ z j + ^ j + lJ
i, h - (i, 2h + n, 2h + i, 2h +i, 2h \
u U + U + U U
2i+l,2j+l - ^ hj i+h3 ij+l + i+l,j+l)
The inter-grid transfers from fine grid Q^ to coarse grid i?2/i a r e generally
1
called restriction operators and are denoted by iff .
u2h = j2h uh (4.5.39)
The simplest restriction operator called injection and defined by
N
,2h
Ui5 = U*i,2j l<i,3< (4.5.40)
allows the values on coarse grid to obtain their values directly from the corre-
sponding fine grid points.
An alternate restriction operator is called full weighting; it is defined by
u w u u u
i,j = jg [ 2i-l,2j-l + 2i-l,2j+l + 2i+l,2j-l + 2i+l,2j+l
u
+ 2 ( ^ j 2 j - l + *4,2j+l + 2i-l,2j + <4+l,2j)
+ 4 < 2 i l l < < , J < ^ r - l (4-5.41)