Page 347 - Computational Fluid Dynamics for Engineers
P. 347
11.5 Model Problem: Sudden Expansion Laminar Duct Flow 337
symmetry line
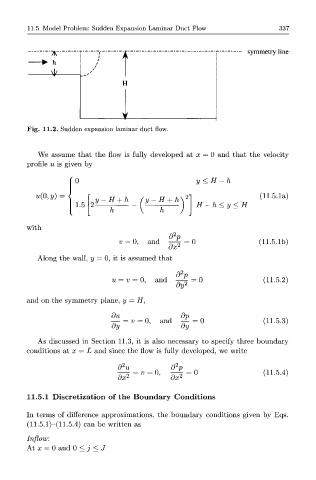
Fig. 11.2. Sudden expansion laminar duct flow.
We assume that the flow is fully developed at x = 0 and that the velocity
profile u is given by
( 0 y<H-h
u(0,y) 2 (11.5.1a)
y-H + h (y-H + h^ ^
1.5 H-h<y<H
h
with
2
d p
v — 0, and —-^ = 0 (11.5.1b)
Along the wall, y = 0, it is assumed that
2
d p
u = v = 0, and -^—^ = 0 (11.5.2)
2
dy
and on the symmetry plane, y = H,
du dp
v = 0, and — = 0 (11.5.3)
dy dy
As discussed in Section 11.3, it is also necessary to specify three boundary
conditions at x — L and since the flow is fully developed, we write
2
2
d u _ d p
(11.5.4)
dx 2 ' dx 2
11.5.1 Discretization of he Boundary Conditions
t
In terms of difference approximations, the boundary conditions given by Eqs.
(11.5.1)—(11.5.4) can be written as
Inflow:
At x = 0 and 0 < j < J