Page 199 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 199
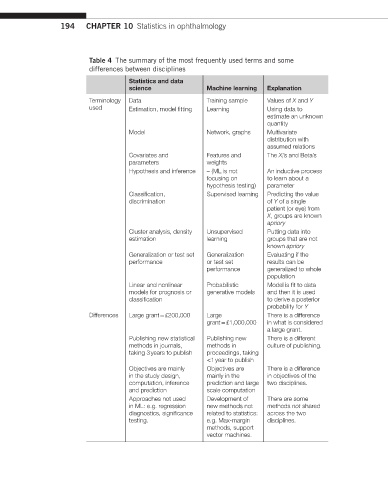
194 CHAPTER 10 Statistics in ophthalmology
Table 4 The summary of the most frequently used terms and some
differences between disciplines
Statistics and data
science Machine learning Explanation
Terminology Data Training sample Values of X and Y
used Estimation, model fitting Learning Using data to
estimate an unknown
quantity
Model Network, graphs Multivariate
distribution with
assumed relations
Covariates and Features and The X i ’s and Beta’s
parameters weights
Hypothesis and inference – (ML is not An inductive process
focusing on to learn about a
hypothesis testing) parameter
Classification, Supervised learning Predicting the value
discrimination of Y of a single
patient (or eye) from
X, groups are known
apriory
Cluster analysis, density Unsupervised Putting data into
estimation learning groups that are not
known apriory
Generalization or test set Generalization Evaluating if the
performance or test set results can be
performance generalized to whole
population
Linear and nonlinear Probabilistic Model is fit to data
models for prognosis or generative models and then it is used
classification to derive a posterior
probability for Y
Differences Large grant = £200,000 Large There is a difference
grant = £1,000,000 in what is considered
a large grant.
Publishing new statistical Publishing new There is a different
methods in journals, methods in culture of publishing.
taking 3 years to publish proceedings, taking
<1 year to publish
Objectives are mainly Objectives are There is a difference
in the study design, mainly in the in objectives of the
computation, inference prediction and large two disciplines.
and prediction scale computation
Approaches not used Development of There are some
in ML: e.g. regression new methods not methods not shared
diagnostics, significance related to statistics: across the two
testing. e.g. Max-margin disciplines.
methods, support
vector machines.