Page 73 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 73
64 CHAPTER 4 Retinal image preprocessing, enhancement, and registration
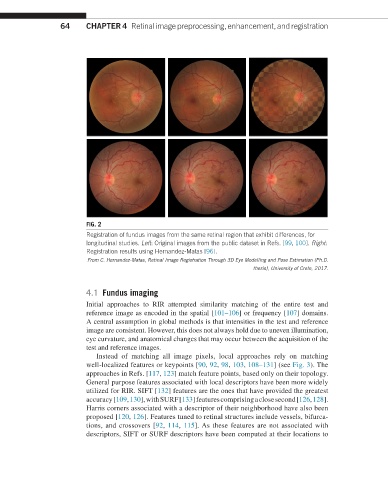
FIG. 2
Registration of fundus images from the same retinal region that exhibit differences, for
longitudinal studies. Left: Original images from the public dataset in Refs. [99, 100]. Right:
Registration results using Hernandez-Matas [96].
From C. Hernandez-Matas, Retinal Image Registration Through 3D Eye Modelling and Pose Estimation (Ph.D.
thesis), University of Crete, 2017.
4.1 Fundus imaging
Initial approaches to RIR attempted similarity matching of the entire test and
reference image as encoded in the spatial [101–106] or frequency [107] domains.
A central assumption in global methods is that intensities in the test and reference
image are consistent. However, this does not always hold due to uneven illumination,
eye curvature, and anatomical changes that may occur between the acquisition of the
test and reference images.
Instead of matching all image pixels, local approaches rely on matching
well-localized features or keypoints [90, 92, 98, 103, 108–131] (see Fig. 3). The
approaches in Refs. [117, 123] match feature points, based only on their topology.
General purpose features associated with local descriptors have been more widely
utilized for RIR. SIFT [132] features are the ones that have provided the greatest
accuracy [109, 130], with SURF [133] features comprising a close second [126, 128].
Harris corners associated with a descriptor of their neighborhood have also been
proposed [120, 126]. Features tuned to retinal structures include vessels, bifurca-
tions, and crossovers [92, 114, 115]. As these features are not associated with
descriptors, SIFT or SURF descriptors have been computed at their locations to