Page 190 -
P. 190
160 CHAPTER 5 / INTERNAL MEMORY
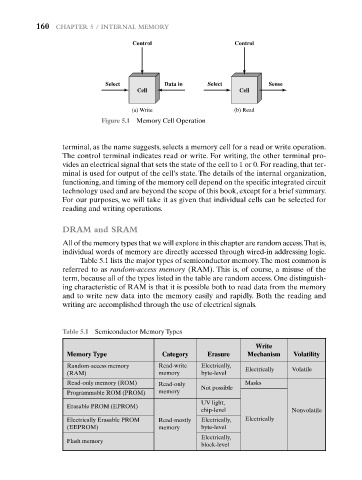
Control Control
Select Data in Select Sense
Cell Cell
(a) Write (b) Read
Figure 5.1 Memory Cell Operation
terminal, as the name suggests, selects a memory cell for a read or write operation.
The control terminal indicates read or write. For writing, the other terminal pro-
vides an electrical signal that sets the state of the cell to 1 or 0. For reading, that ter-
minal is used for output of the cell’s state. The details of the internal organization,
functioning, and timing of the memory cell depend on the specific integrated circuit
technology used and are beyond the scope of this book, except for a brief summary.
For our purposes, we will take it as given that individual cells can be selected for
reading and writing operations.
DRAM and SRAM
All of the memory types that we will explore in this chapter are random access.That is,
individual words of memory are directly accessed through wired-in addressing logic.
Table 5.1 lists the major types of semiconductor memory.The most common is
referred to as random-access memory (RAM). This is, of course, a misuse of the
term, because all of the types listed in the table are random access. One distinguish-
ing characteristic of RAM is that it is possible both to read data from the memory
and to write new data into the memory easily and rapidly. Both the reading and
writing are accomplished through the use of electrical signals.
Table 5.1 Semiconductor Memory Types
Write
Memory Type Category Erasure Mechanism Volatility
Random-access memory Read-write Electrically,
Electrically Volatile
(RAM) memory byte-level
Read-only memory (ROM) Read-only Masks
Programmable ROM (PROM) memory Not possible
UV light,
Erasable PROM (EPROM)
chip-level Nonvolatile
Electrically Erasable PROM Read-mostly Electrically, Electrically
(EEPROM) memory byte-level
Electrically,
Flash memory
block-level