Page 229 -
P. 229
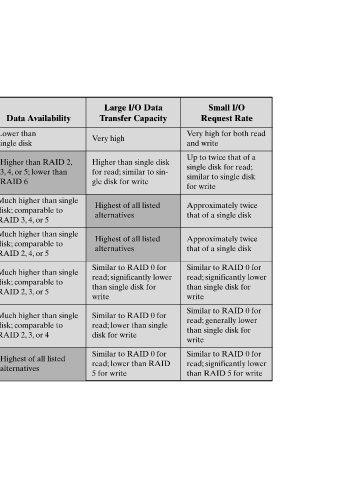
Small I/O Request Rate Very high for both read and write Up to twice that of a single disk for read; similar to single disk for write Approximately twice that of a single disk Approximately twice that of a single disk Similar to RAID 0 for significantly lower read; than single disk for write Similar to RAID 0 for generally lower read; than single disk for write Similar to RAID 0 for significantly lower read; than RAID 5 for write
Large I/O Data Transfer Capacity Very high Higher than single disk similar to sin- for read; gle disk for write Highest of all listed alternatives Highest of all listed alternatives Similar to RAID 0 for significantly lower read; than single disk for write Similar to RAID 0 for lower than single read; disk for write Similar to RAID 0 for lower than RAID read; 5 for write
Data Availability Lower than single disk Higher than RAID 2, lower than or 5; 4, 3, RAID 6 Much higher than single comparable to disk; or 5 4, RAID 3, Much higher than single comparable to disk; or 5 4, RAID 2, Much higher than single comparable to disk; or 5 3, RAID 2, Much higher than single comparable to disk; or 4 3, RAID 2, Highest of all listed alternatives
Disks Required N 2N m + N 1 + N 1 + N 1 + N 2 + N
Description Nonredundant Mirrored Redundant via Ham- ming code parity Bit-interleaved Block-interleaved parity Block-interleaved distributed parity Block-interleaved dual distributed parity proportional to log N
RAID Levels Level 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 m number of data disks;
Table 6.3 Category Striping Mirroring Parallel access Independent access = N
196