Page 46 -
P. 46
2.1 / A BRIEF HISTORY OF COMPUTERS 23
Start
Is next
Yes No
instruction MAR PC
No memory in IBR?
Fetch access
cycle
required
MBR M(MAR)
Left IBR MBR (20:39)
IR IBR (0:7) IR MBR (20:27) No instruction Yes
MAR IBR (8:19) MAR MBR (28:39) required? IR MBR (0:7)
MAR MBR (8:19)
PC PC + 1
Decode instruction in IR
AC M(X) Go to M(X, 0:19) If AC > 0 then AC AC + M(X)
go to M(X, 0:19)
Execution Yes Is AC > 0?
cycle
MBR M(MAR) PC MAR MBR M(MAR)
AC MBR AC AC + MBR
M(X) = contents of memory location whose address is X
(i:j) = bits i through j
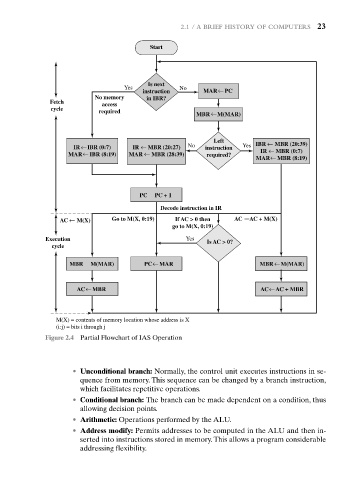
Figure 2.4 Partial Flowchart of IAS Operation
• Unconditional branch: Normally, the control unit executes instructions in se-
quence from memory. This sequence can be changed by a branch instruction,
which facilitates repetitive operations.
• Conditional branch: The branch can be made dependent on a condition, thus
allowing decision points.
• Arithmetic: Operations performed by the ALU.
• Address modify: Permits addresses to be computed in the ALU and then in-
serted into instructions stored in memory. This allows a program considerable
addressing flexibility.