Page 308 -
P. 308
Section 9.3 Image Segmentation by Clustering Pixels 276
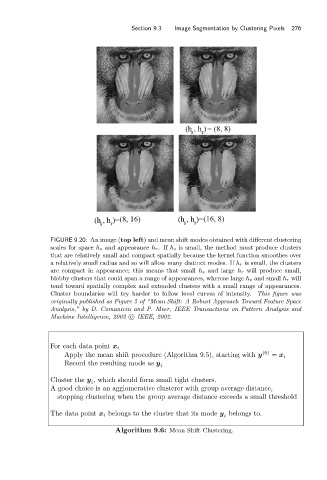
(h ,h) = (8, 8)
s r
(h ,h)= (8, 16) (h ,h)= (16, 8)
s r s r
FIGURE 9.20: An image (top left) and mean shift modes obtained with different clustering
scales for space h s and appearance h r.If h s is small, the method must produce clusters
that are relatively small and compact spatially because the kernel function smoothes over
a relatively small radius and so will allow many distinct modes. If h r is small, the clusters
are compact in appearance; this means that small h s and large h r will produce small,
blobby clusters that could span a range of appearances, whereas large h s and small h r will
tend toward spatially complex and extended clusters with a small range of appearances.
Cluster boundaries will try harder to follow level curves of intensity. This figure was
originally published as Figure 5 of “Mean Shift: A Robust Approach Toward Feature Space
Analysis,” by D. Comaniciu and P. Meer, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 2002 c IEEE, 2002.
For each data point x i
Apply the mean shift procedure (Algorithm 9.5), starting with y (0) = x i
Record the resulting mode as y i
Cluster the y , which should form small tight clusters.
i
A good choice is an agglomerative clusterer with group average distance,
stopping clustering when the group average distance exceeds a small threshold
The data point x i belongs to the cluster that its mode y belongs to.
i
Algorithm 9.6: Mean Shift Clustering.