Page 104 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 104
Electrochemical Power
time, in units of ampere hours (Ah). The energy capacity in watt hours is
the ampere-hour capacity multiplied by the battery voltage.
A battery with a rating of 20 Ah can provide 20 A for 1 h, or 1 A for 20 h,
or 100 mA (100 milliamperes) for 200 h.The limitations are shelf life at one
extreme, and maximum deliverable current at the other. Shelf life is the
length of time the battery will remain usable if it is never connected to a
load; this is measured in months or years.The maximum deliverable current
is the highest current a battery can drive through a load without the voltage
dropping significantly because of the battery’s own internal resistance.
Small cells have storage capacity of a few milliampere hours (mAh) up
to 100 or 200 mAh. Medium-sized cells might supply 500 mAh to 1000
mAh (1 Ah). Large automotive lead–acid batteries can provide upwards
of 100 Ah.
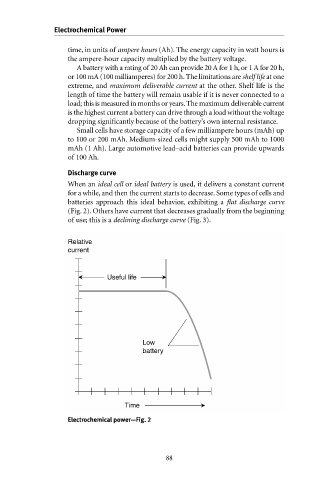
Discharge curve
When an ideal cell or ideal battery is used, it delivers a constant current
for a while, and then the current starts to decrease. Some types of cells and
batteries approach this ideal behavior, exhibiting a flat discharge curve
(Fig. 2). Others have current that decreases gradually from the beginning
of use; this is a declining discharge curve (Fig. 3).
Relative
current
Useful life
Low
battery
Time
Electrochemical power—Fig. 2