Page 108 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 108
Electrostatic Transducer
Devices that convert sound into electricity, or vice versa, are another
form of electromechanical transducer. Speakers and microphones are uni-
versal examples. They usually work by means of dynamic principles, but
some work by electrostatic interactions.
Galvanometer-type analog meters,also known as D’Arsonval meters, are
electromechanical transducers.They convert electric current into displace-
ment.In recent years,digital meters have largely replaced electromechanical
meters. Digital devices do not have moving parts to wear out, so they last
much longer than electromechanical types. Digital meters are also able to
tolerate more physical abuse.
Robots use electromechanical transducers in many ways. Examples
include the selsyn, the stepper motor, and the servomechanism.
See also SELSYN, STEPPER MOTOR, and SERVOMECHANISM.
ELECTROSTATIC TRANSDUCER
An electrostatic transducer is a device that changes mechanical energy into
electrical energy or vice versa by taking advantage of electrostatic forces.
The most common types involve conversion between sound waves and
audio-frequency electric currents.
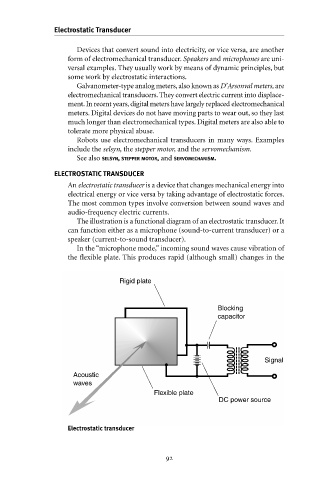
The illustration is a functional diagram of an electrostatic transducer. It
can function either as a microphone (sound-to-current transducer) or a
speaker (current-to-sound transducer).
In the “microphone mode,” incoming sound waves cause vibration of
the flexible plate. This produces rapid (although small) changes in the
Rigid plate
Blocking
capacitor
Signal
Acoustic
waves
Flexible plate
DC power source
Electrostatic transducer