Page 190 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 190
Landmark
move molten metals from vats into molds. They can also be used to handle
certain types of hazardous material.
Ladle grippers require significant gravitation or acceleration force in
which to operate. For this reason, they are generally not suitable for use
in outer space. Also, the material being moved must have a significantly
greater density than the medium in which the movement takes place. For
example,a ladle gripper might be used to move ethanol from one container
to another in air at sea level, but not under water.
See also ROBOT GRIPPER.
LANDMARK
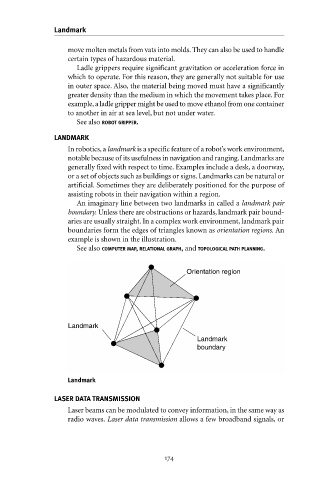
In robotics, a landmark is a specific feature of a robot’s work environment,
notable because of its usefulness in navigation and ranging.Landmarks are
generally fixed with respect to time. Examples include a desk, a doorway,
or a set of objects such as buildings or signs. Landmarks can be natural or
artificial. Sometimes they are deliberately positioned for the purpose of
assisting robots in their navigation within a region.
An imaginary line between two landmarks in called a landmark pair
boundary. Unless there are obstructions or hazards, landmark pair bound-
aries are usually straight. In a complex work environment, landmark pair
boundaries form the edges of triangles known as orientation regions. An
example is shown in the illustration.
See also COMPUTER MAP, RELATIONAL GRAPH, and TOPOLOGICAL PATH PLANNING.
Orientation region
Landmark
Landmark
boundary
Landmark
LASER DATA TRANSMISSION
Laser beams can be modulated to convey information, in the same way as
radio waves. Laser data transmission allows a few broadband signals, or